Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) in an Excel spreadsheet
Watch the Related Videos on Our YouTube Channel (in English):
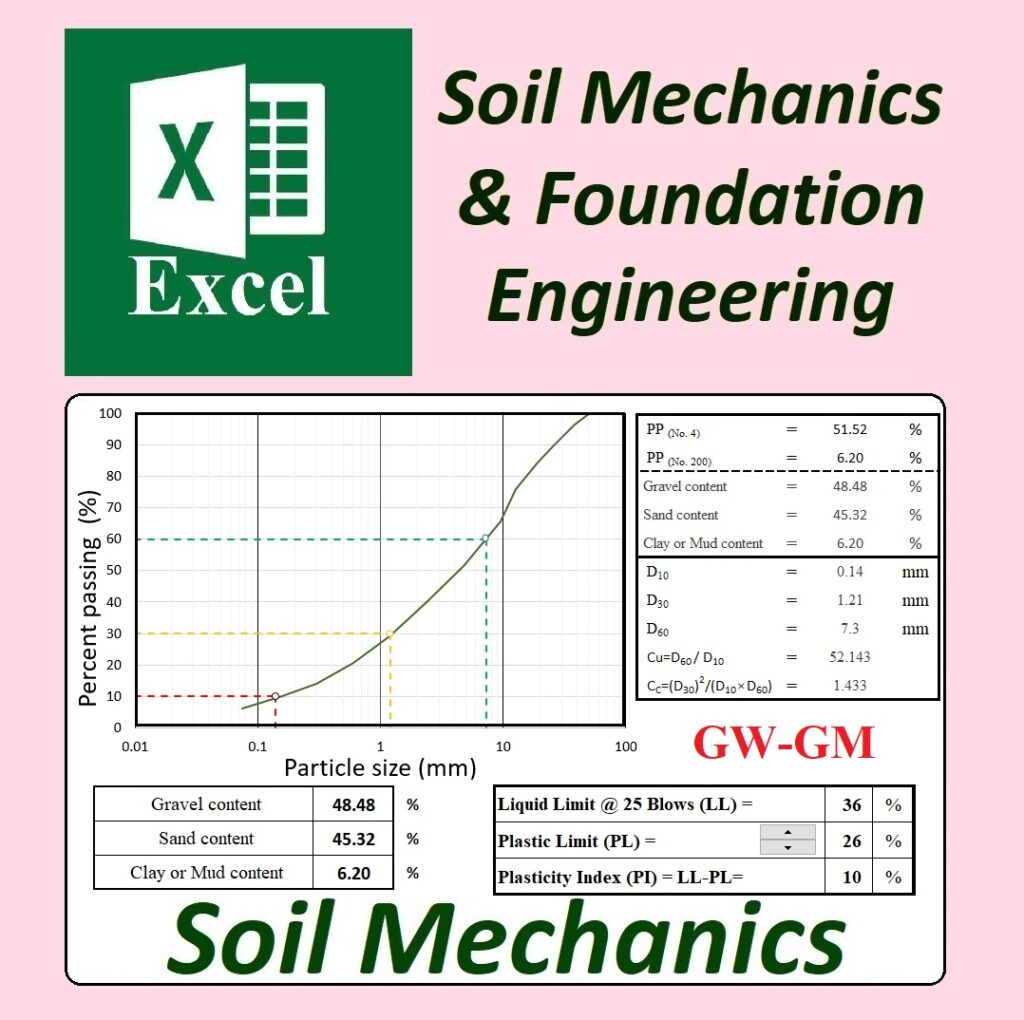
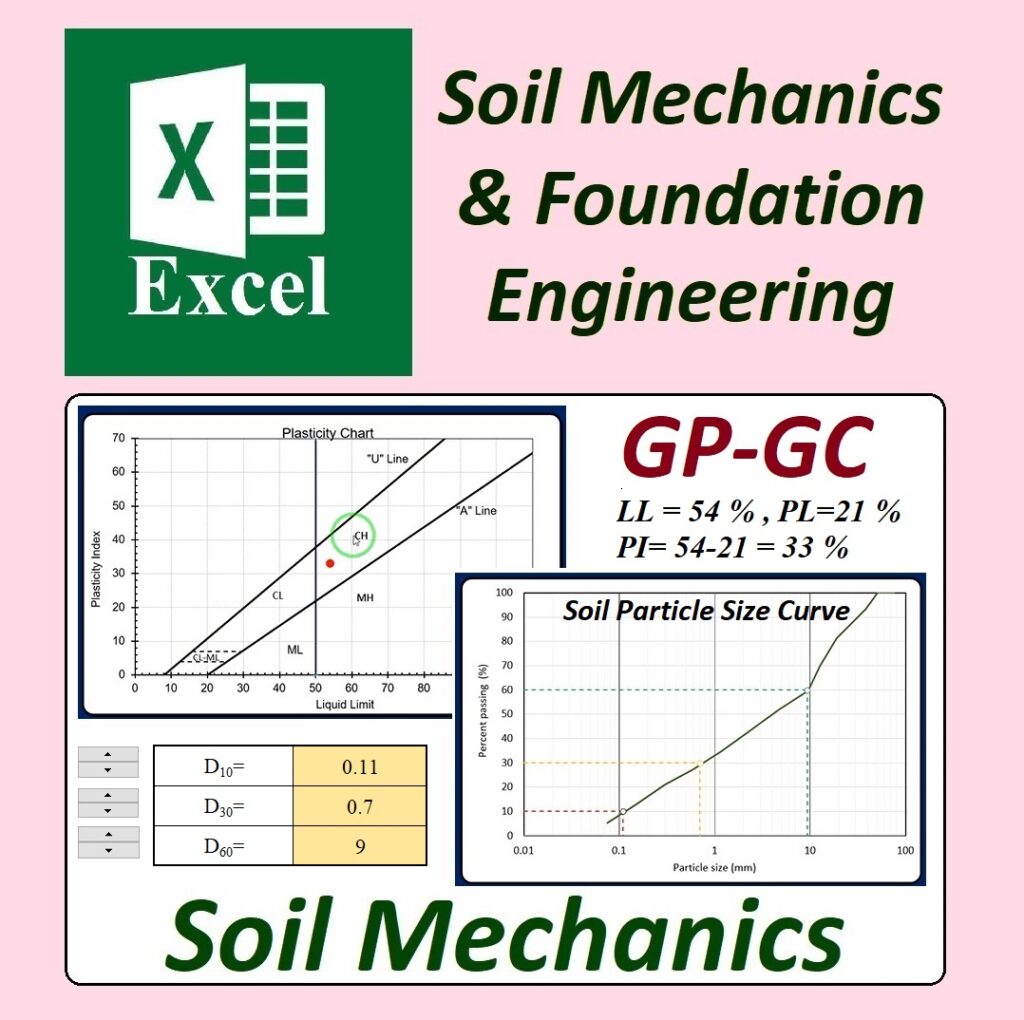
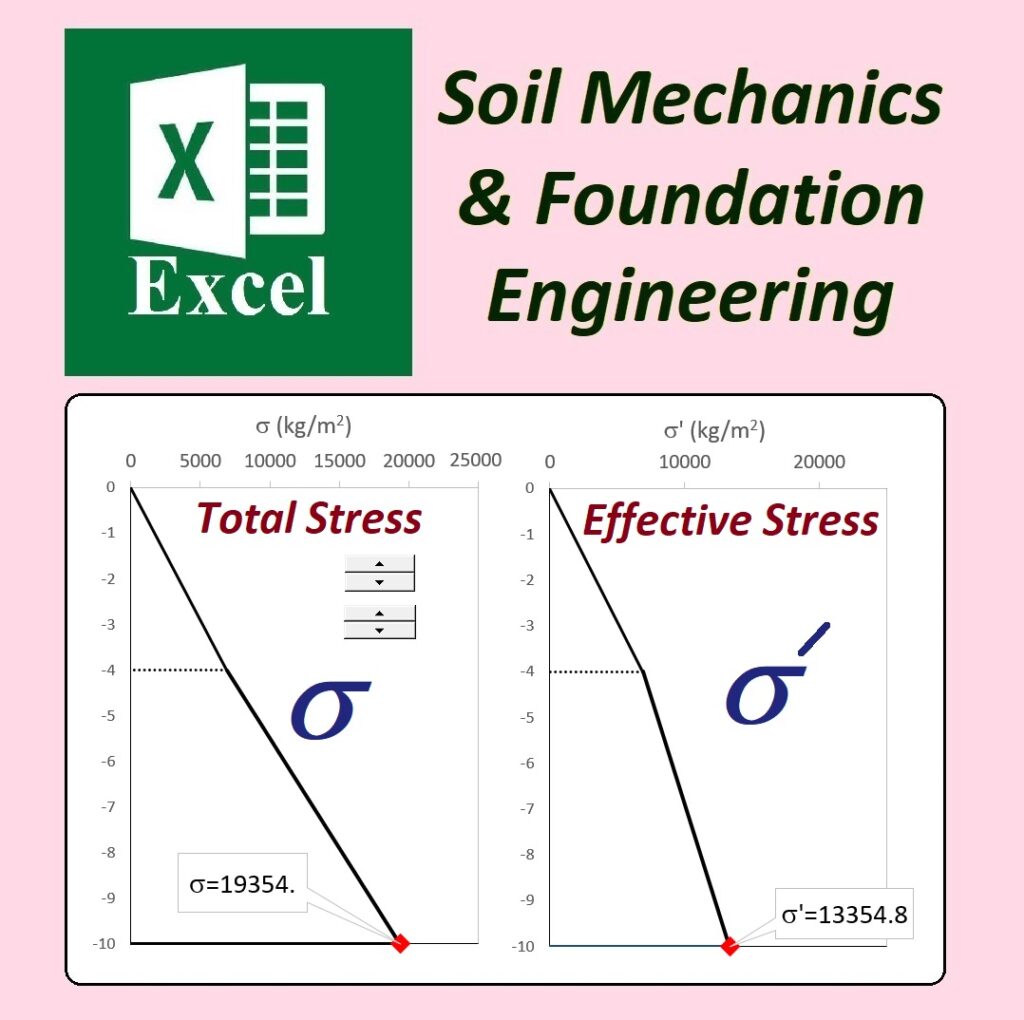
To use the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) in Excel for soil classification in geotechnical engineering, you start by entering soil test data, such as grain size distribution and Atterberg limits, into structured columns. Parameters like particle size percentages and consistency limits are included. Logical formulas are applied to classify the soil based on these data. For example, if over 50% of the particles pass through the No. 200 sieve, the soil is classified as fine-grained; otherwise, it is coarse-grained. Additional criteria like plasticity index and liquid limit further refine the classification into categories like CL, ML, or SM.
GW-GM is a dual classification in USCS, indicating a mix of well-graded gravel (GW) and silty gravel (GM). Well-graded gravel has a wide range of particle sizes, improving compaction and strength, while the silty component suggests the presence of fine particles, which slightly reduces permeability and increases cohesion. This combination provides a balance between stability and drainage, making it suitable for various engineering applications.
✅ Instagram Page Address:
☑ https://www.instagram.com/academy.dr.fahmi
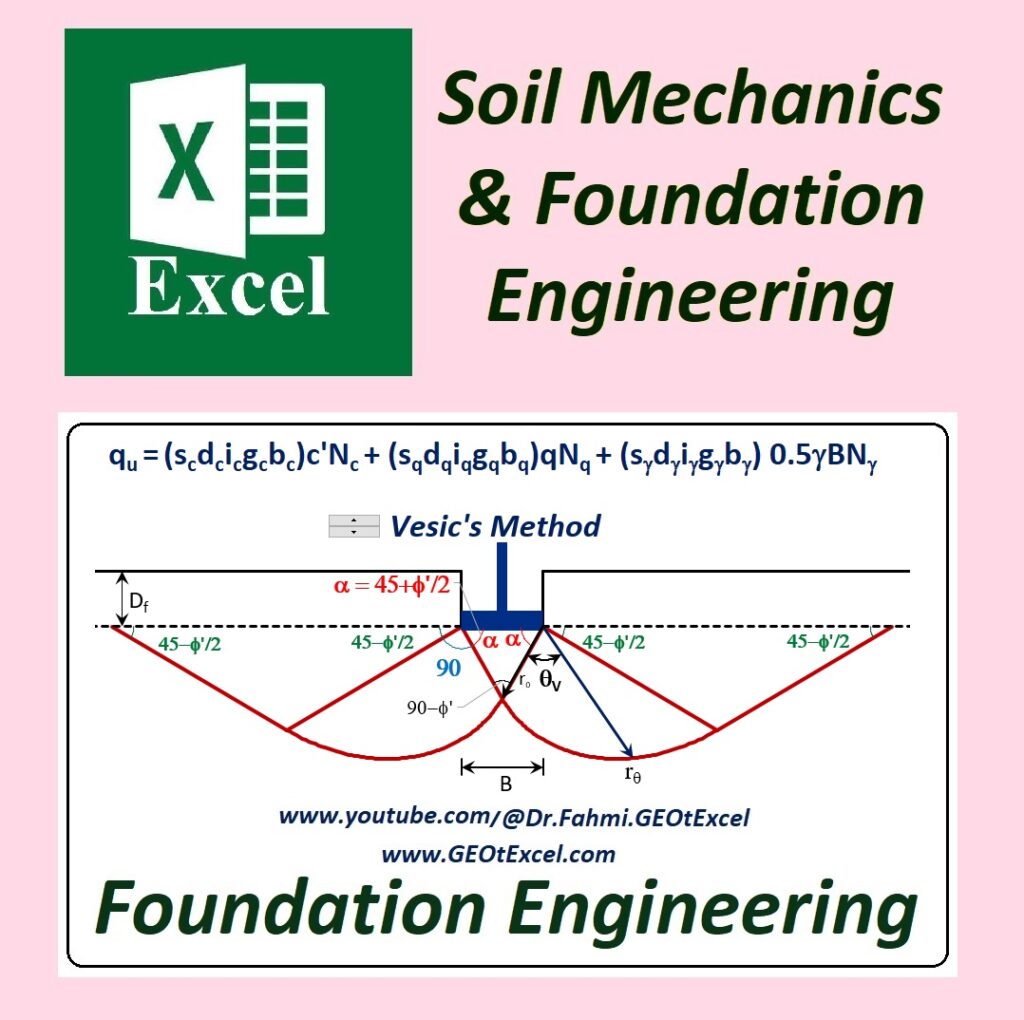
✅ Excel Spreadsheets for Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering
✅ Geotechnical Excel Programs & Lectures
https://www.youtube.com/@Dr.Fahmi.GEOtExcel
Designed by Dr. Ahmad Fahmi