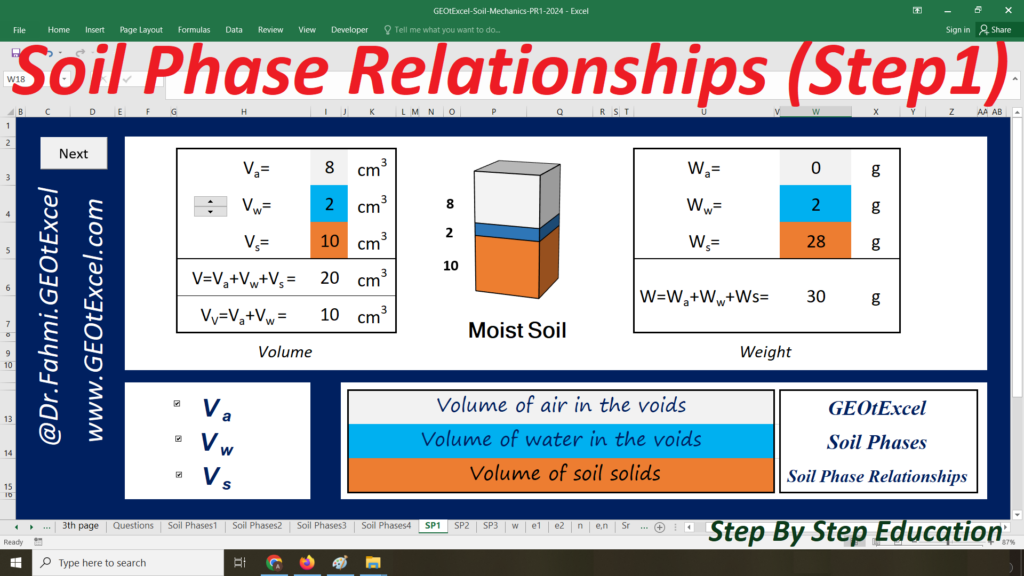
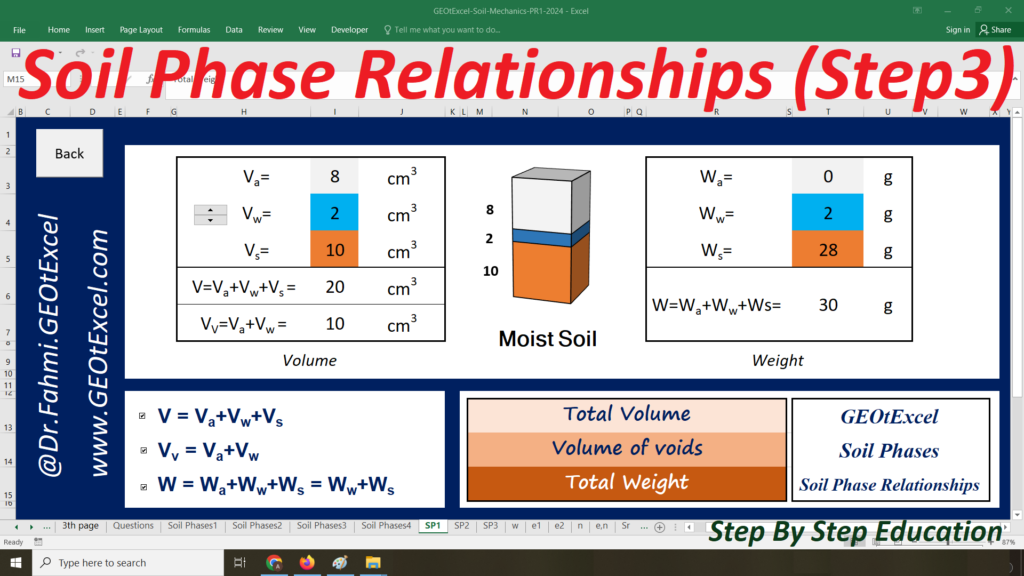
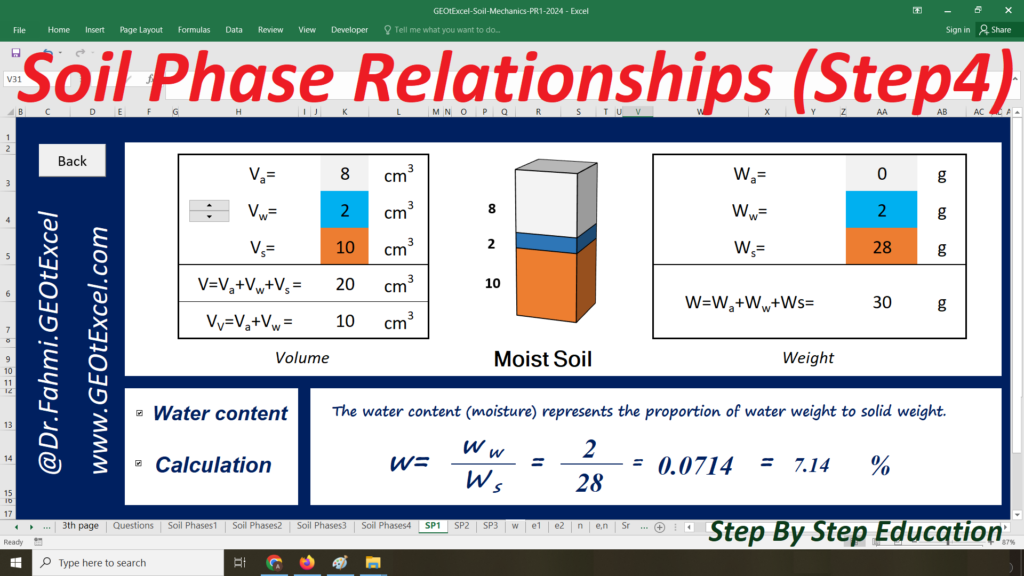
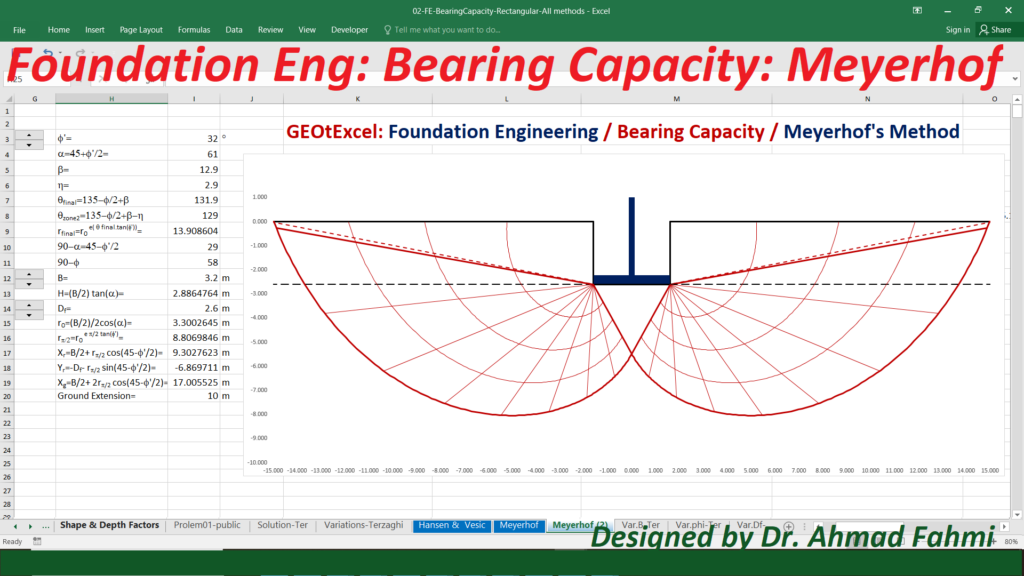
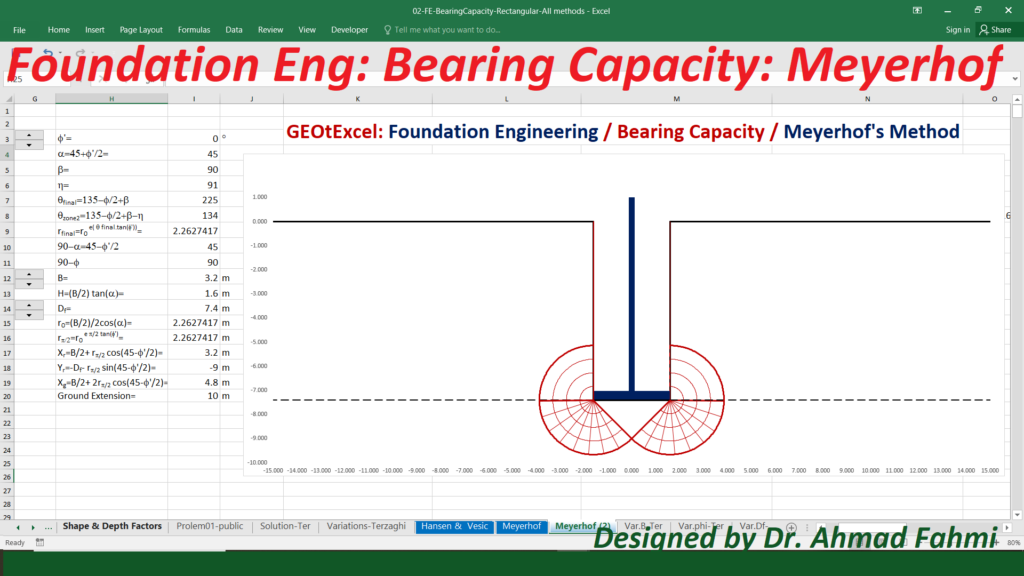
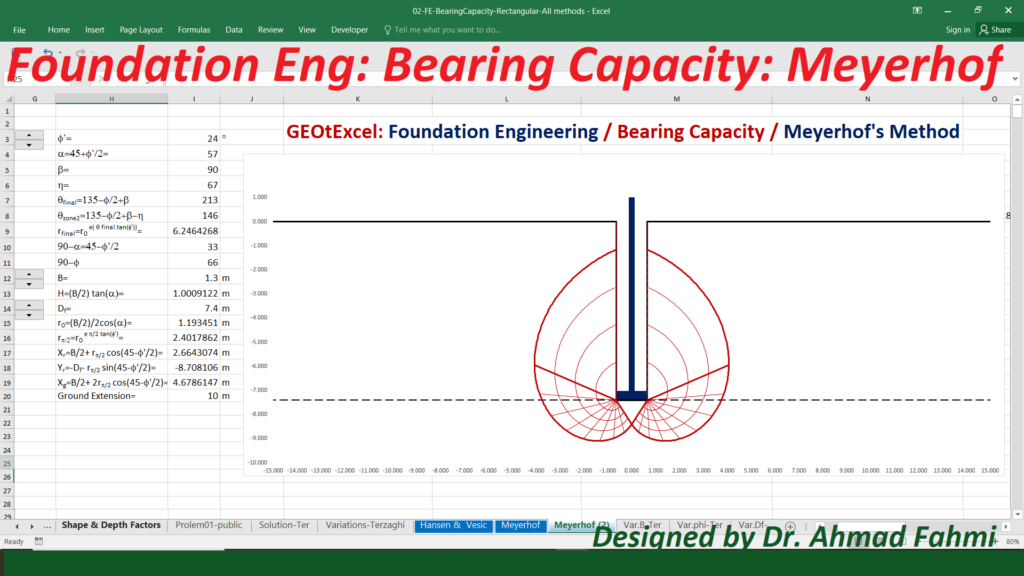
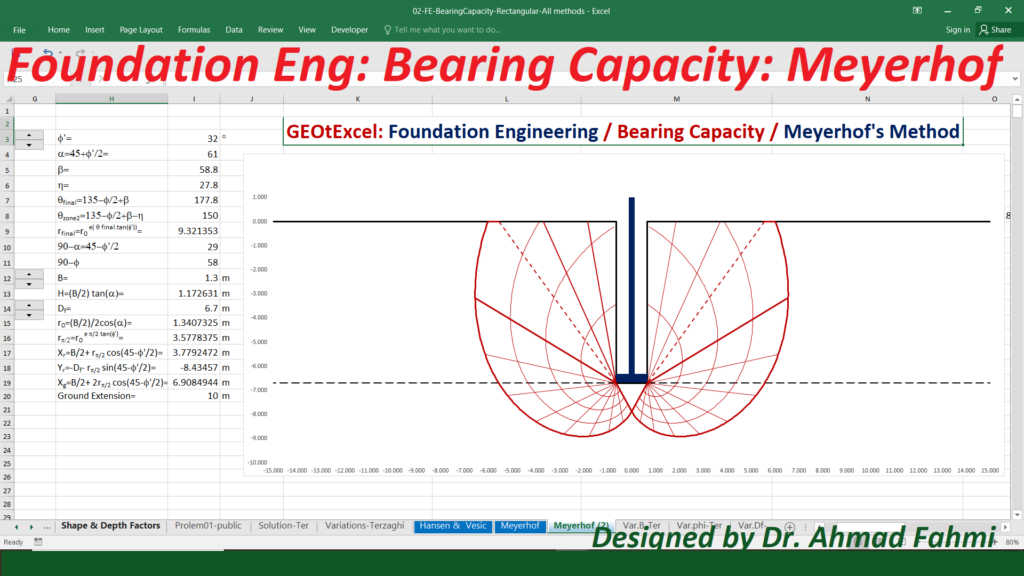
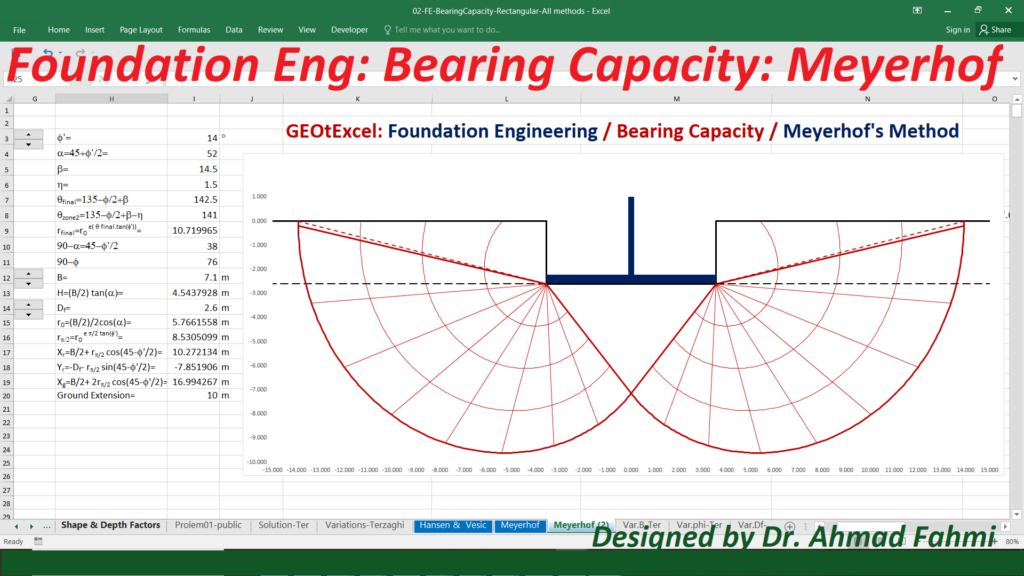
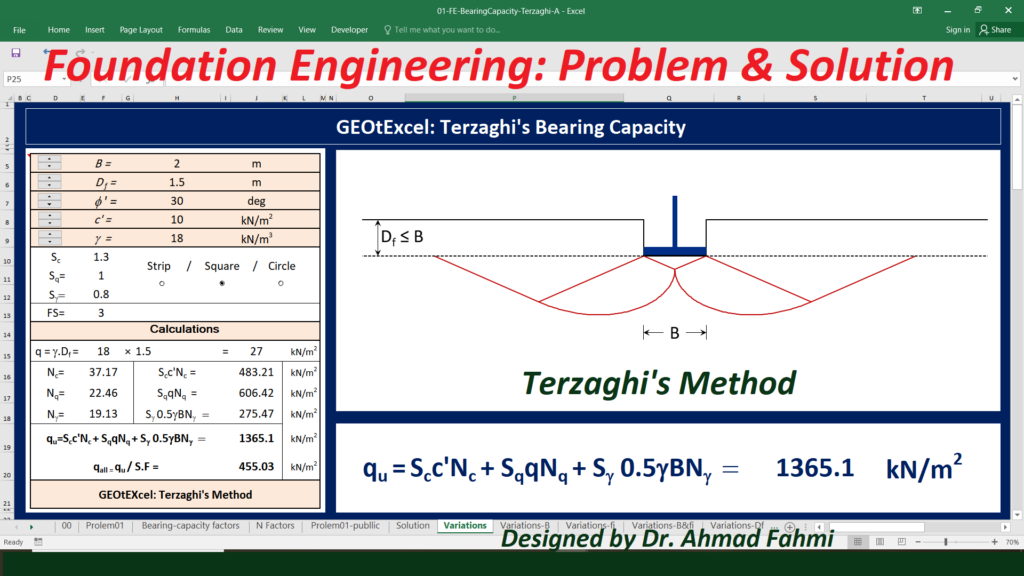
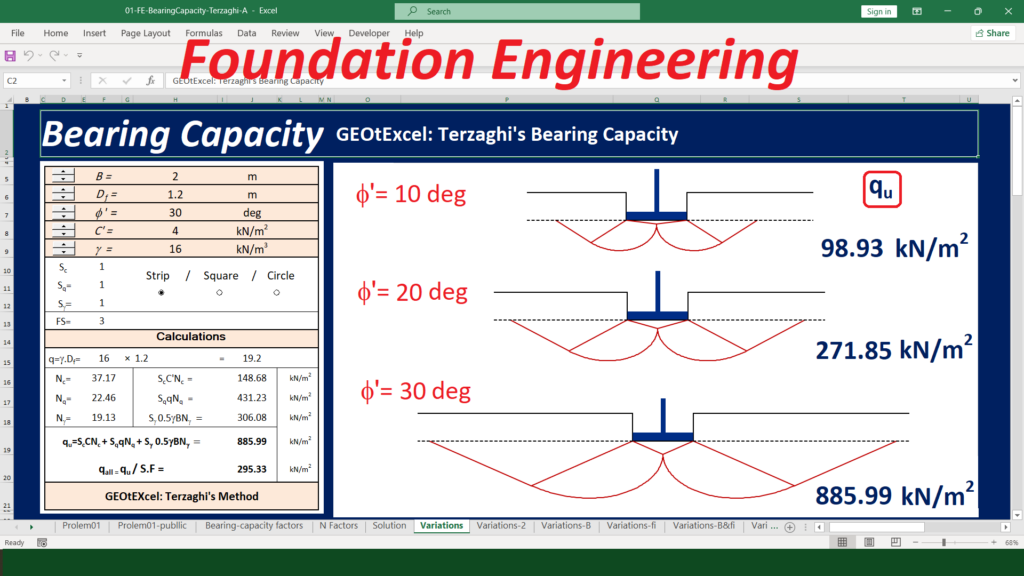
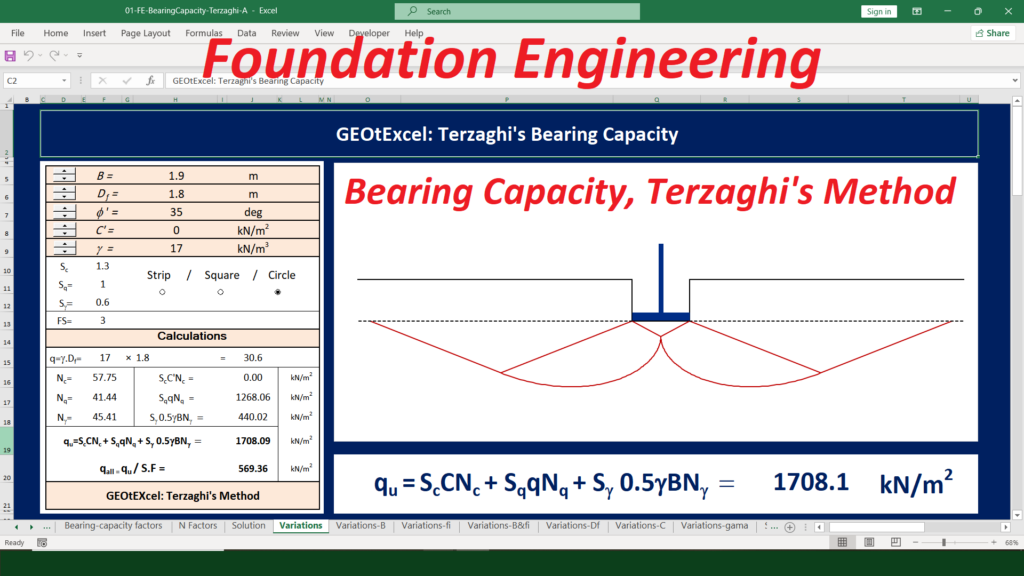
Soil Mechanics – Effective Stress for Single Layer Soil Profile | GEOtExcel Spreadsheets
[GEO-2025-0122] – By Dr. Ahmad Fahmi
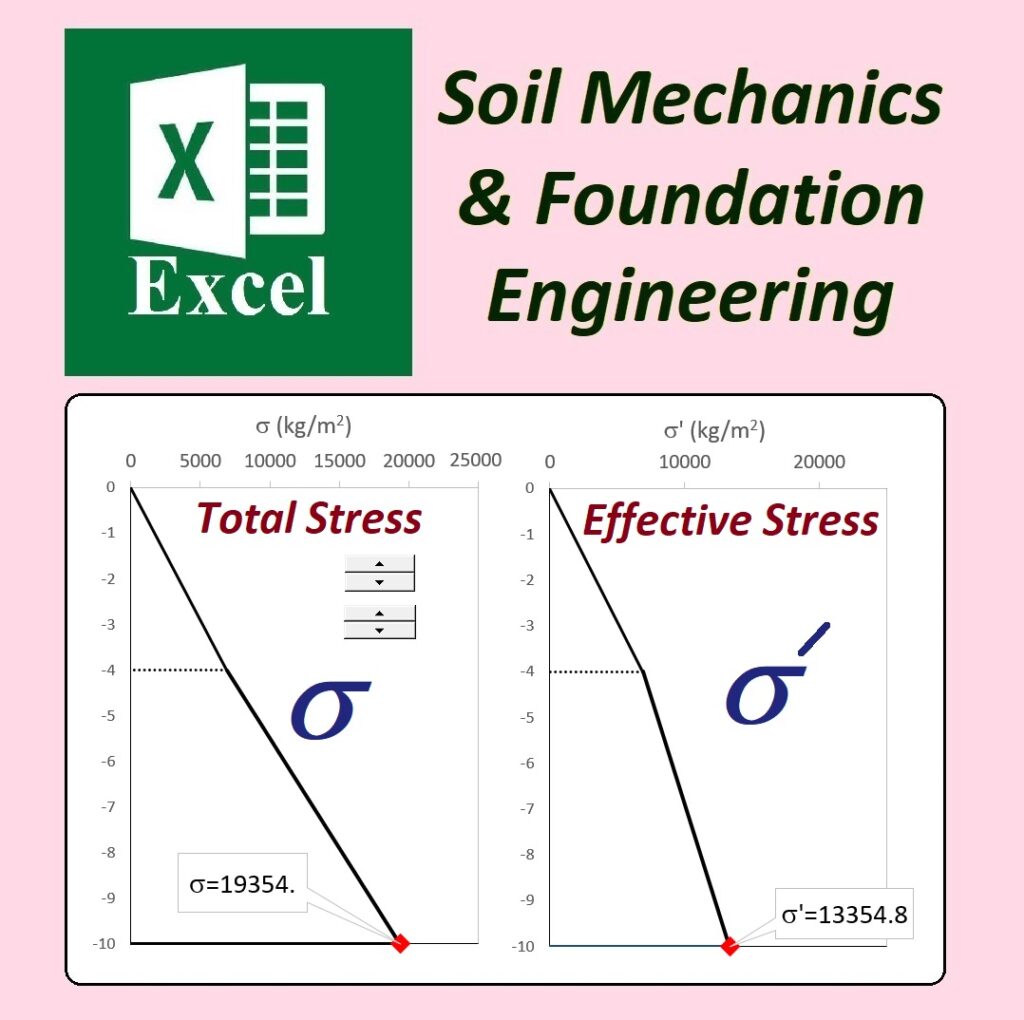
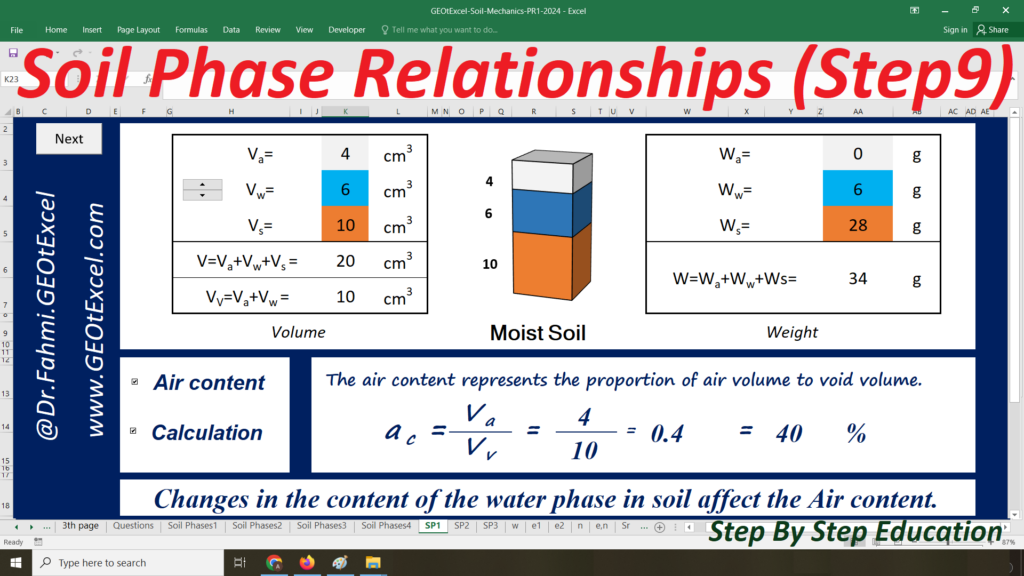
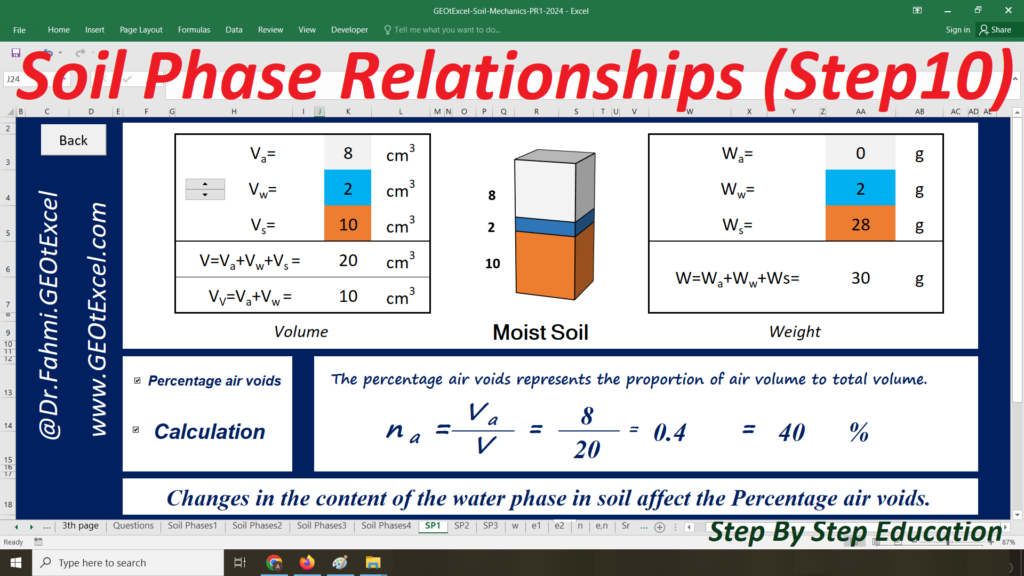
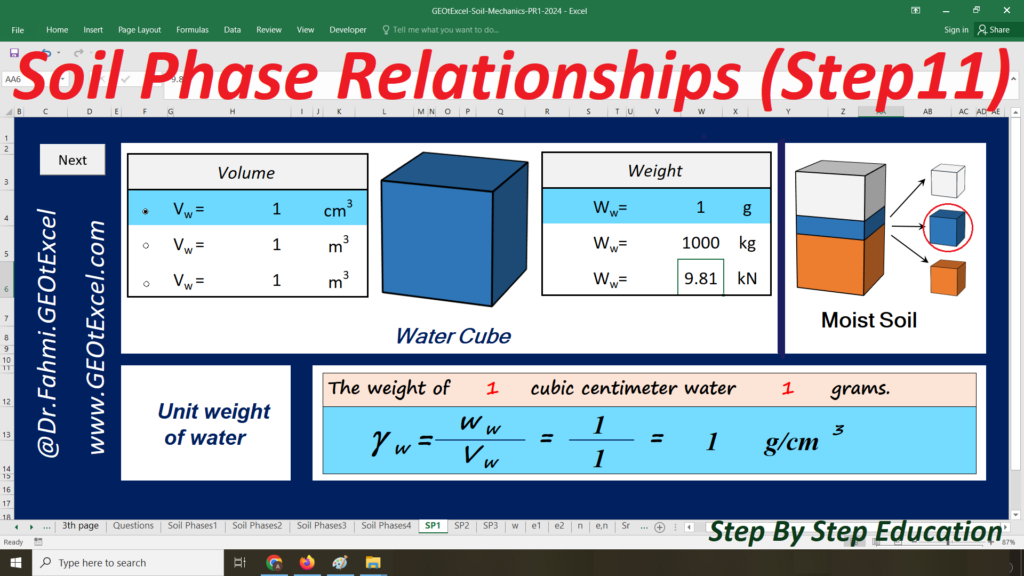
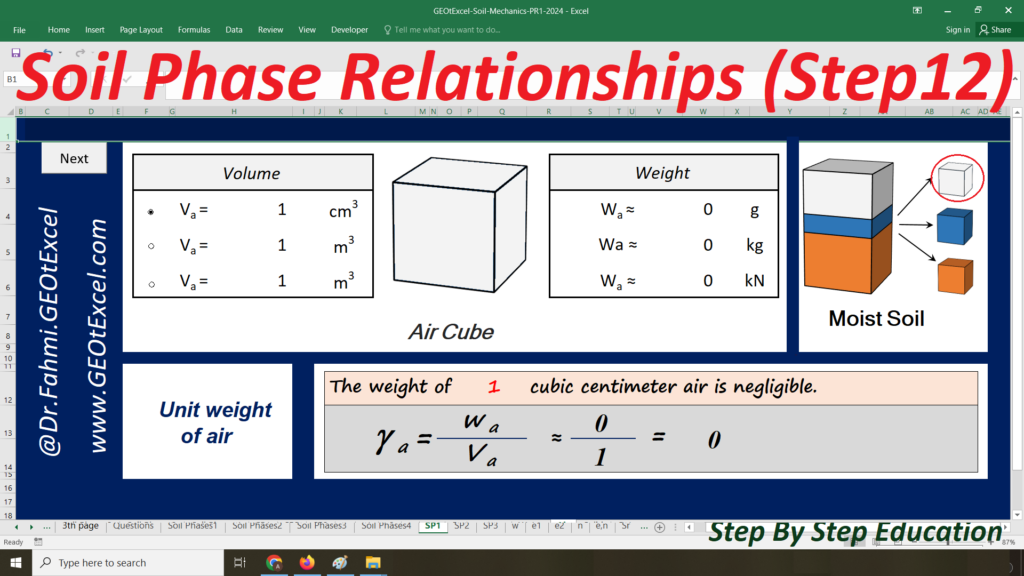
We are excited to present the Effective Stress for Single Layer Soil Profile spreadsheet pack, part of the GEOtExcel (2025-1) collection. This set includes 20 sheets, designed for geotechnical engineers, soil mechanics students, and civil engineers looking to calculate and visualize effective stress in a single-layer soil profile. The pack includes essential calculations and graphs for total stress, pore water pressure, and effective stress in both kg/m² and kN/m² units.
What’s Included in the 20 Spreadsheets?
- Start: Introduction sheet for Effective Stress calculations (kg-Layout 1).
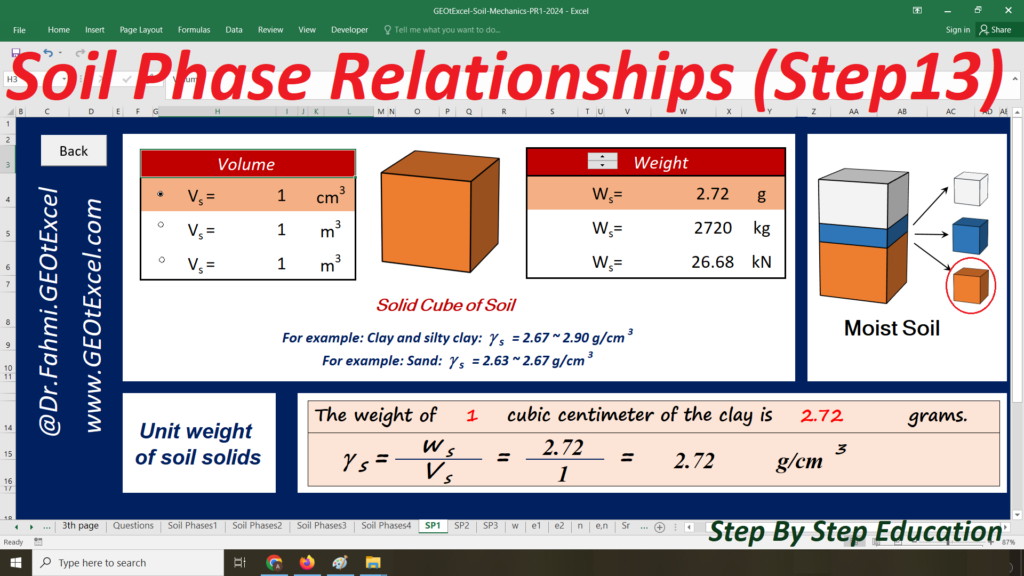
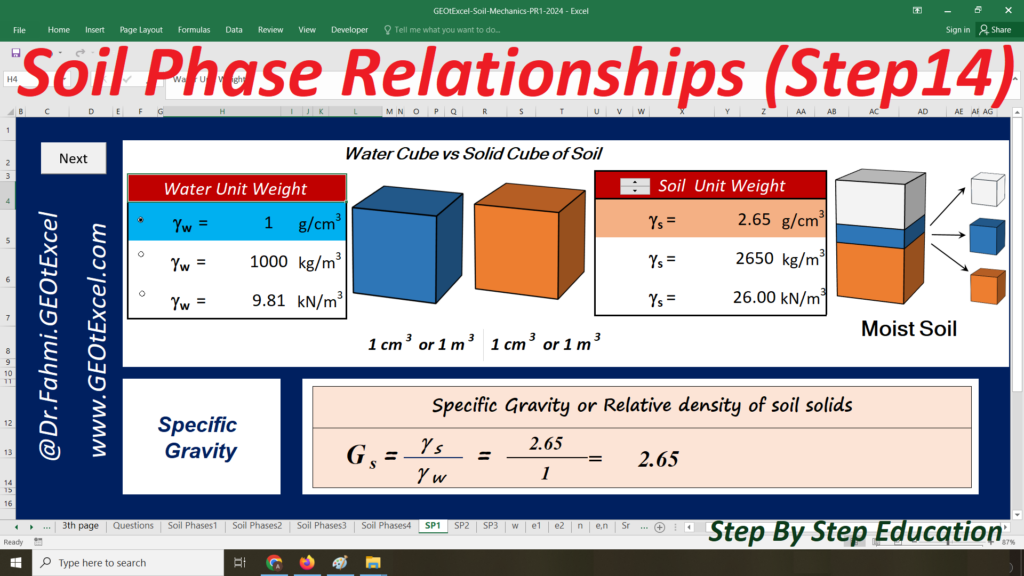
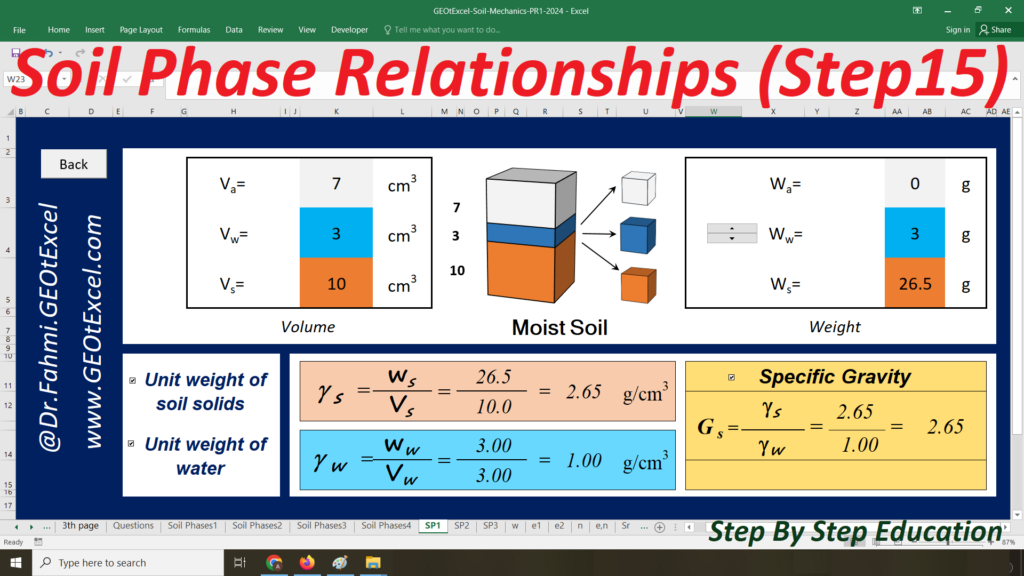
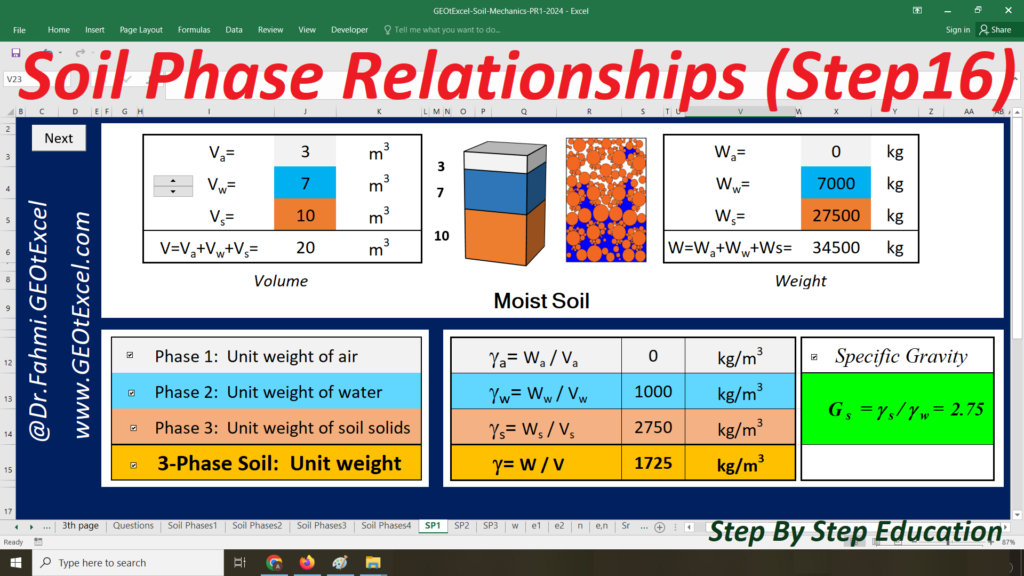
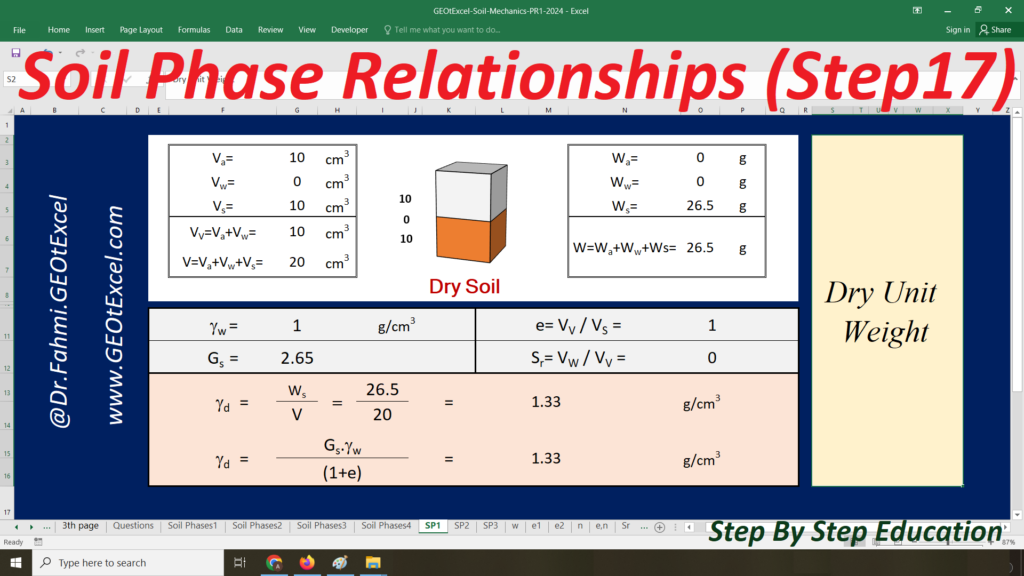
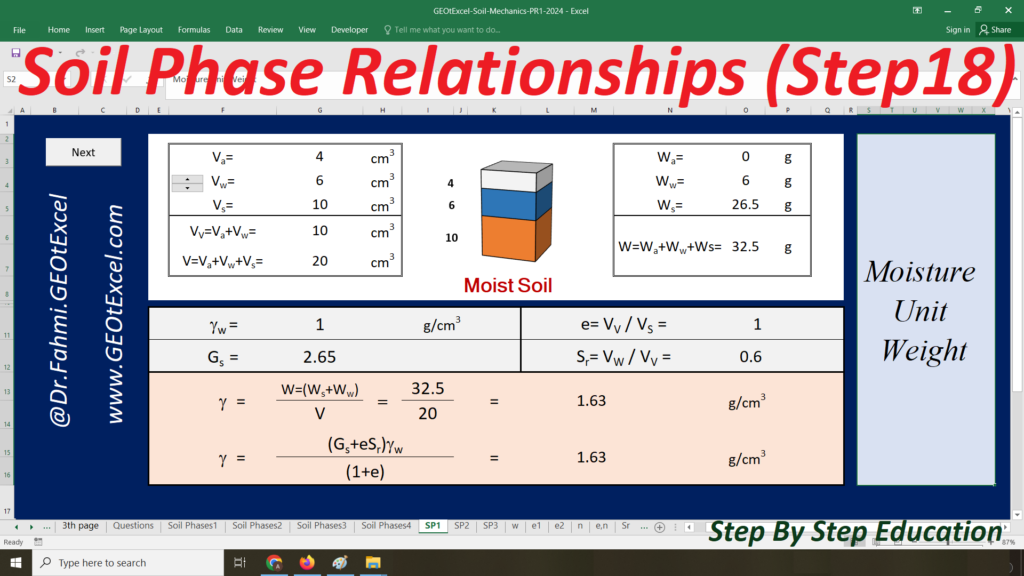
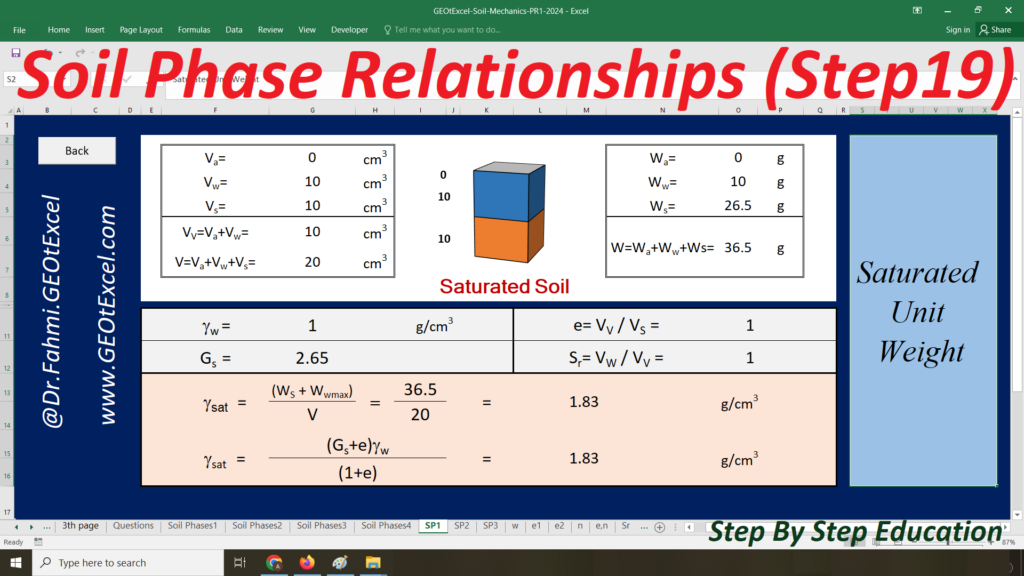
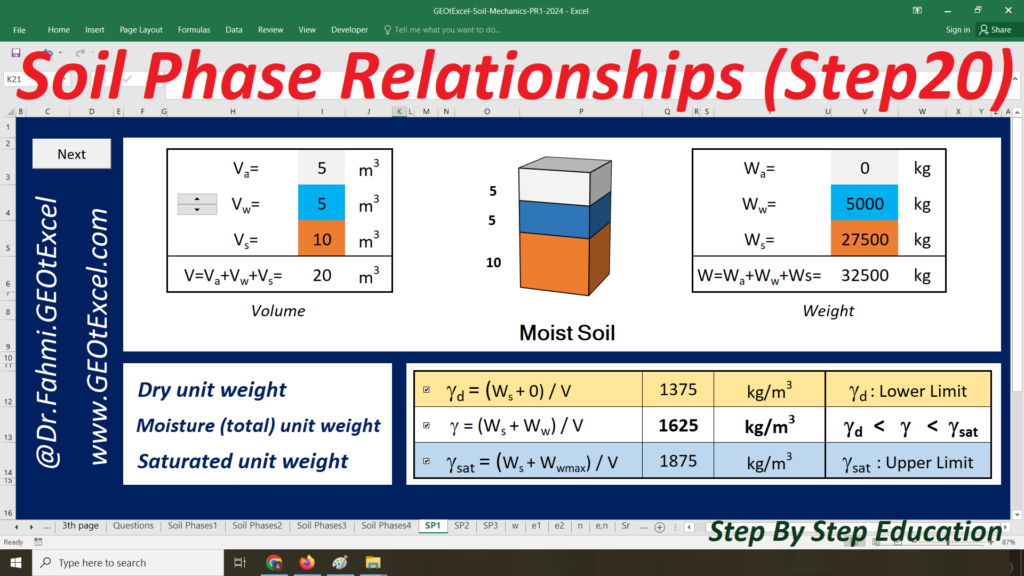
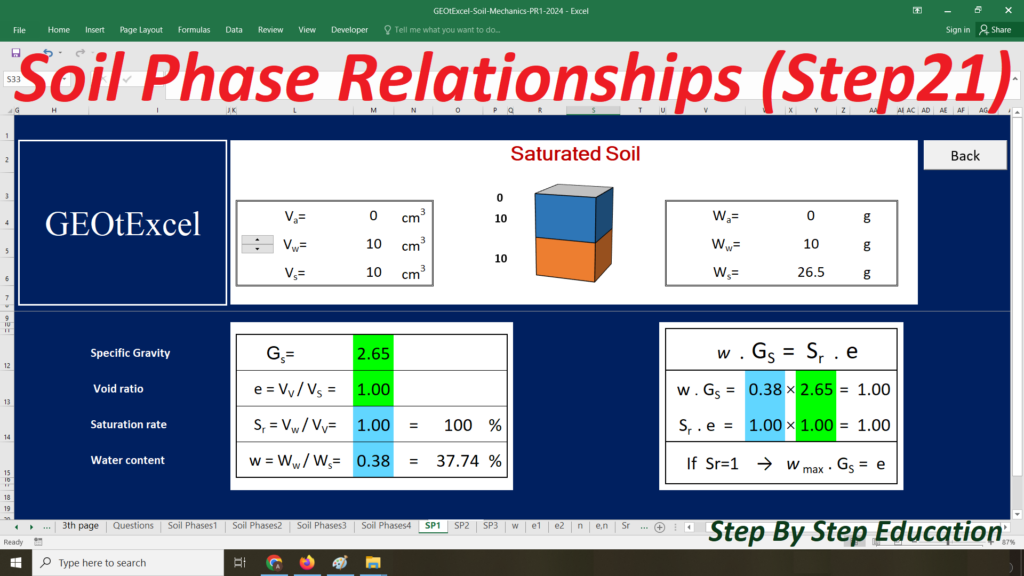
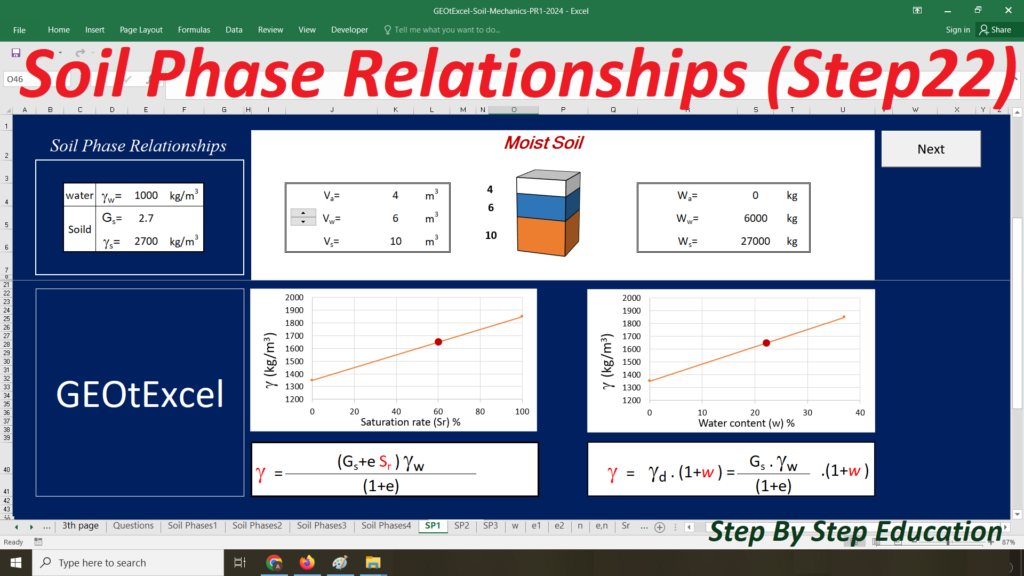
- Single Layer-kg: Main sheet explaining the Effective Stress concept for a single-layer profile in kg/m².
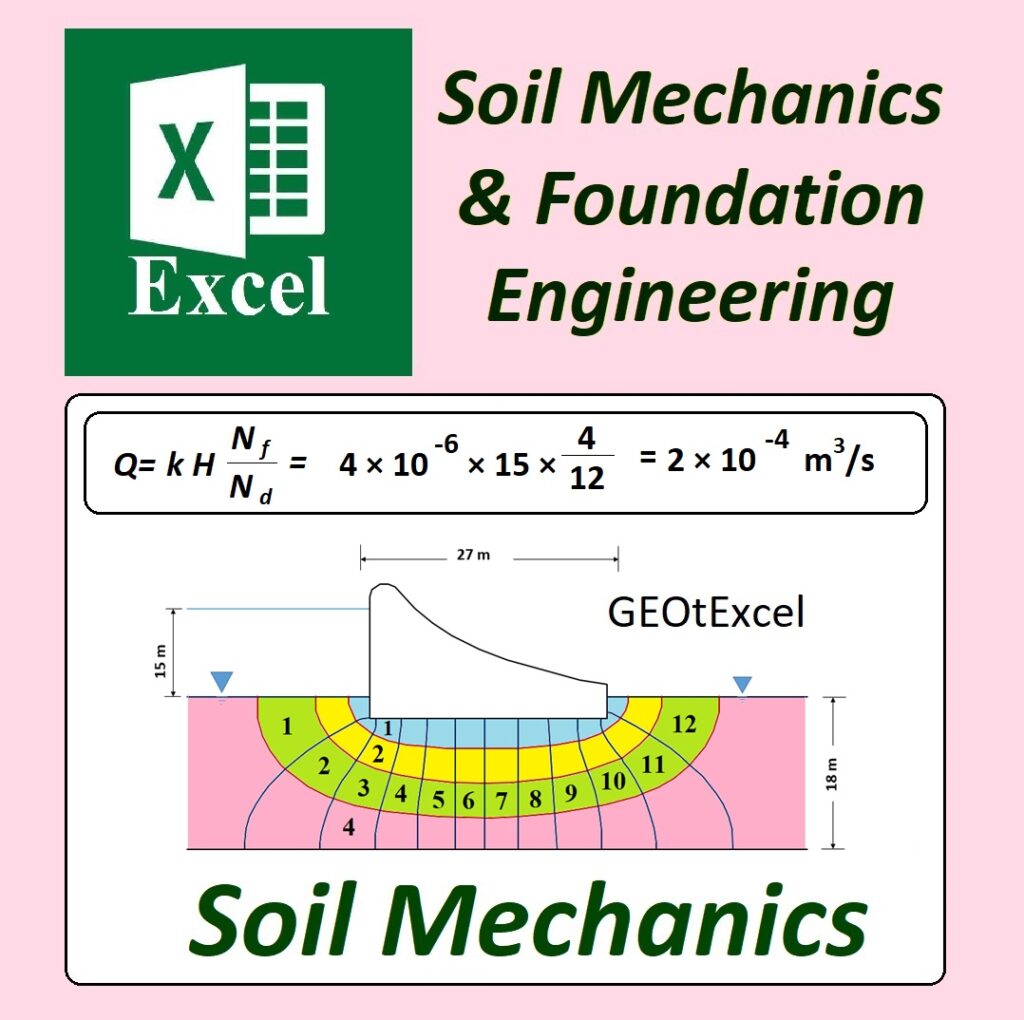
- TS-01: Calculation Sheet 1 for Total Stress calculation and associated graph.
- u-01: Calculation Sheet 2 for Pore Water Pressure calculation and graph.
- ES-01: Calculation Sheet 3 for Effective Stress calculation and graph.
- [GEO-2025-0122-A] – kg-Layout 1: Effective Stress layout for kg/m².
- [GEO-2025-0122-B] – kg-Layout 2: Second layout for Effective Stress using kg/m².
- [GEO-2025-0122-C] – kN-Layout 1: Effective Stress layout for kN/m².
- [GEO-2025-0122-D] – kN-Layout 2: Second layout for Effective Stress using kN/m².
Applications in Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering:
- Performing effective stress analysis in single-layer soil profiles
- Calculating and visualizing total stress, pore water pressure, and effective stress
- Teaching and learning about effective stress concepts in soil mechanics
- Suitable for geotechnical testing, field work, and laboratory experiments
- Ideal for use in civil engineering projects and foundation design
- Comprehensive graphs for visual understanding and data interpretation
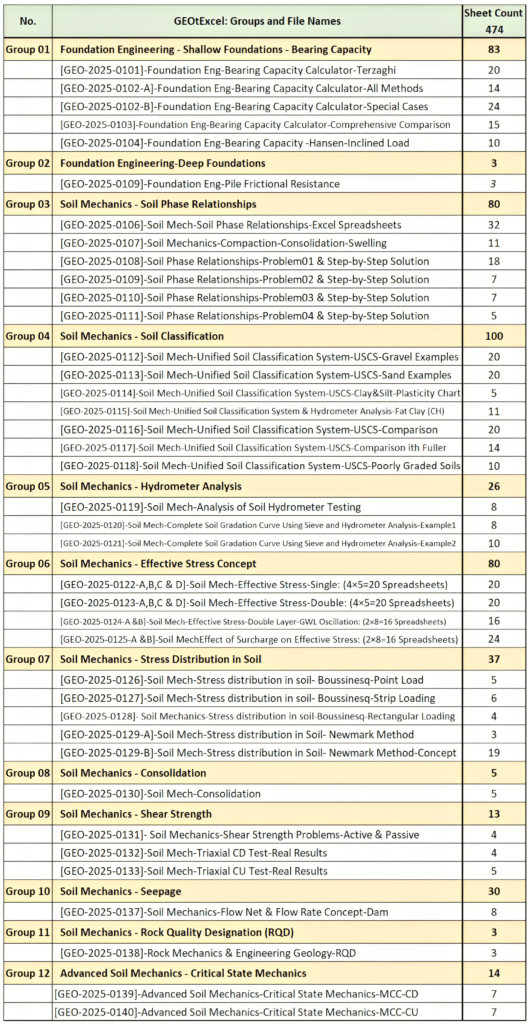
📦 Part of GEOtExcel 2025-1 Collection
This product is part of the GEOtExcel (2025-1) suite, featuring:
- 12 groups of spreadsheets
- 50 files for various soil mechanics and foundation engineering calculations
- 470+ spreadsheets
- Secure and permanent access to all files on your computer
- Commercially licensed for professional use
For more information or to purchase, contact us at:
📧 academy.dr.fahmi@gmail.com
🛒 To Buy GEOtExcel and Use It on Your PC:
👉 How to Buy GEOtExcel and Use It on Your PC
🔗 Follow GEOtExcel on Social Media:
👨🏫 About Dr. Ahmad Fahmi
Assistant Professor, Geotechnical Engineering, University of Bonab
Dr. Fahmi specializes in applying Excel-based solutions for soil mechanics, foundation engineering, and geotechnical testing.
📌 Stay Updated:
Subscribe for upcoming lectures on:
- Soil Mechanics
- Foundation Engineering
- Geotechnical Lab Testing
➡️ Subscribe on YouTube