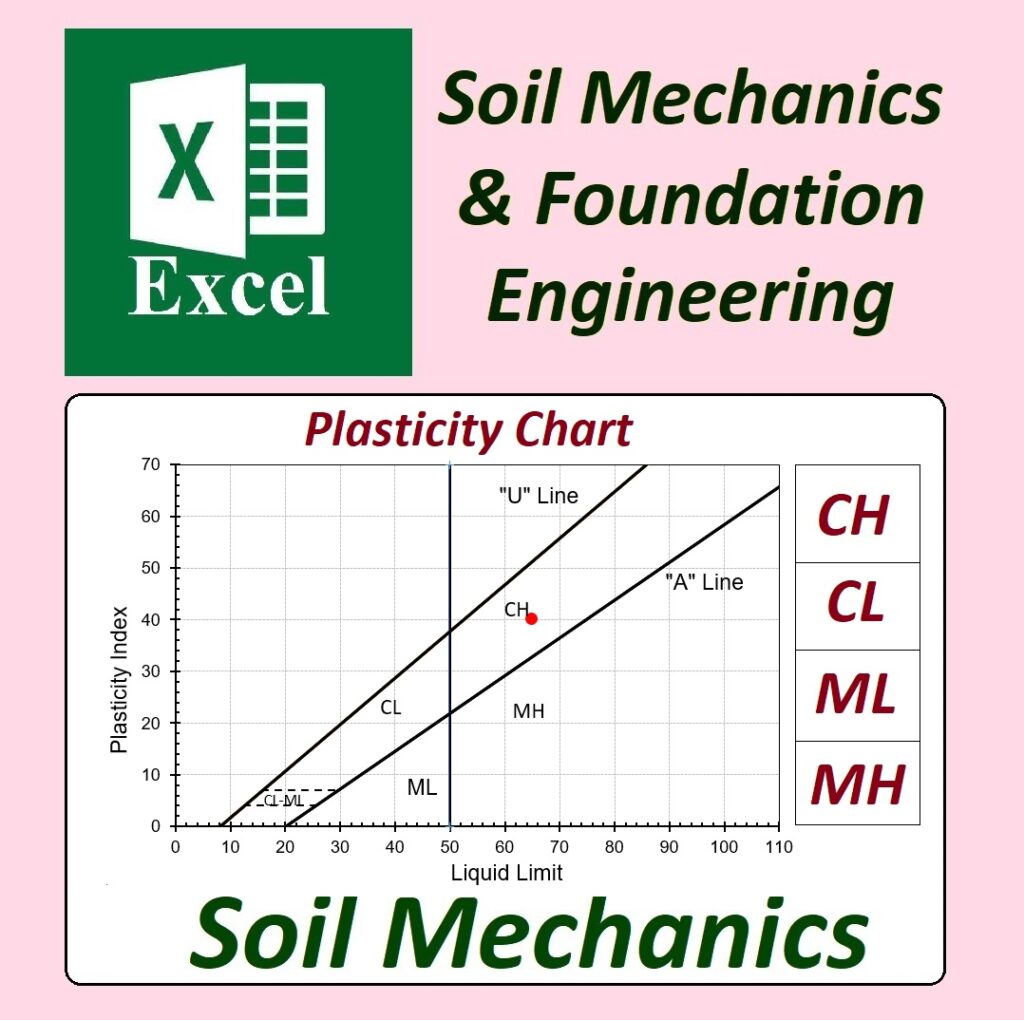
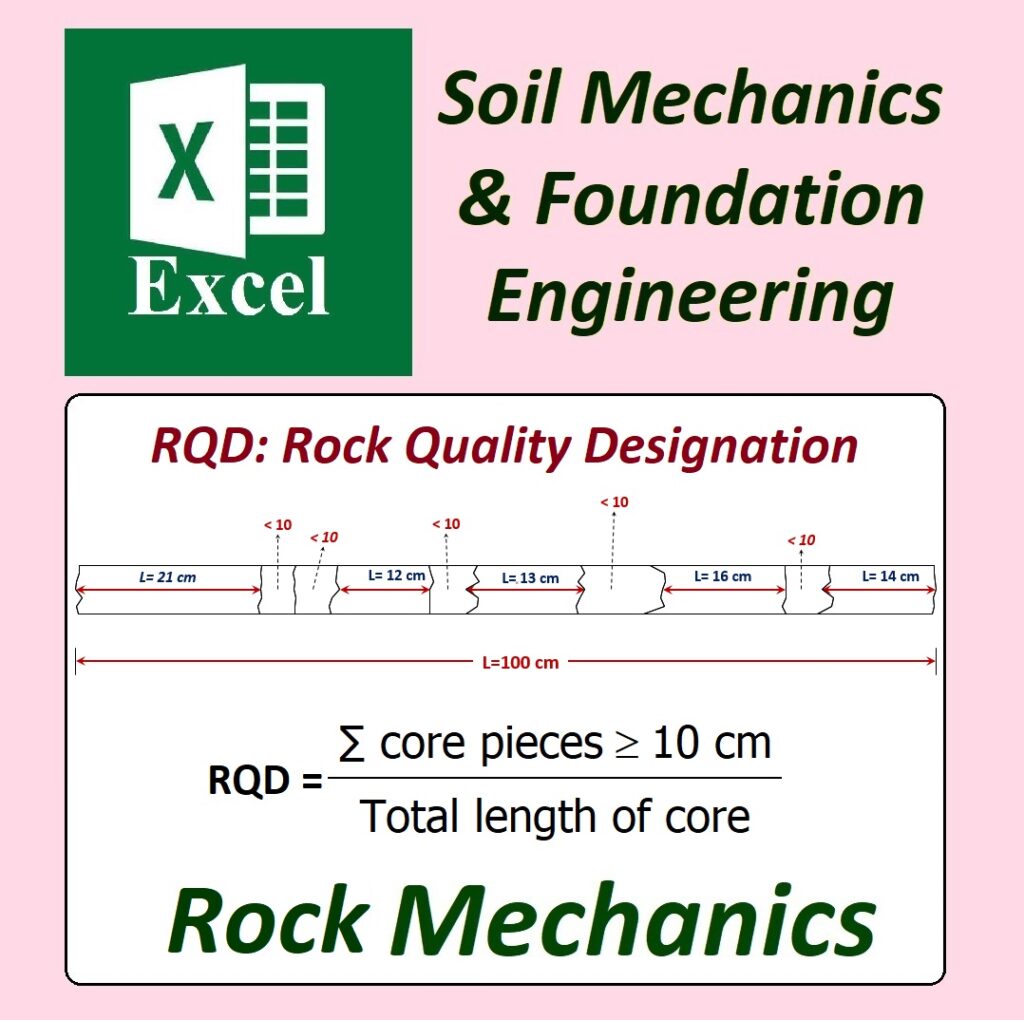
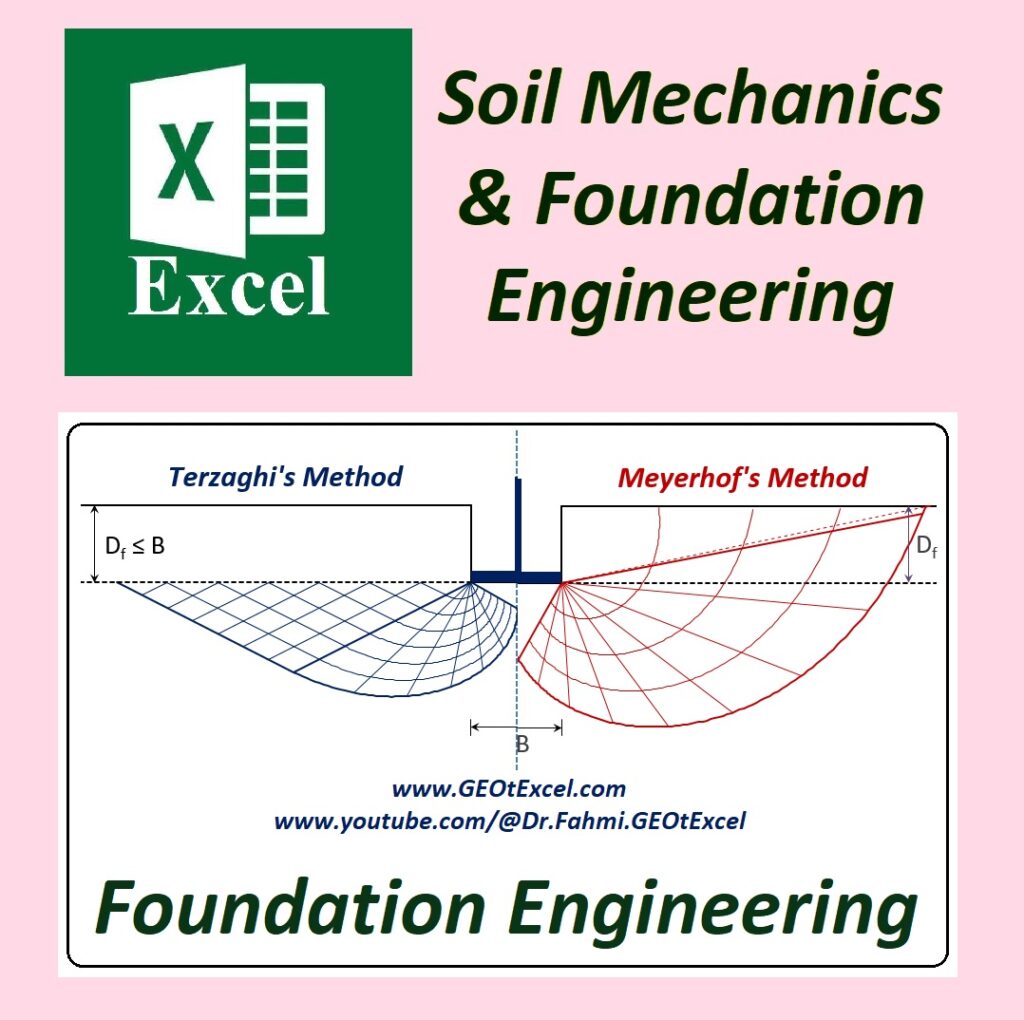
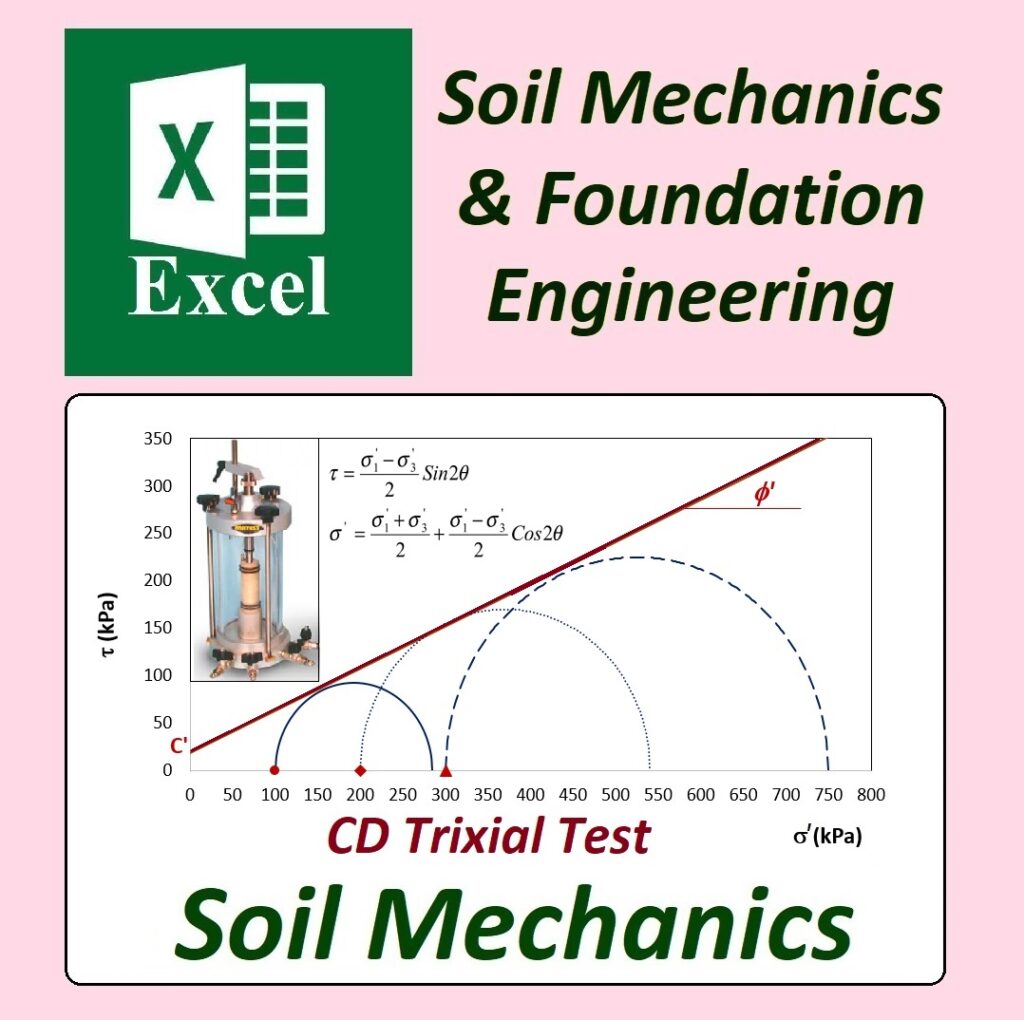
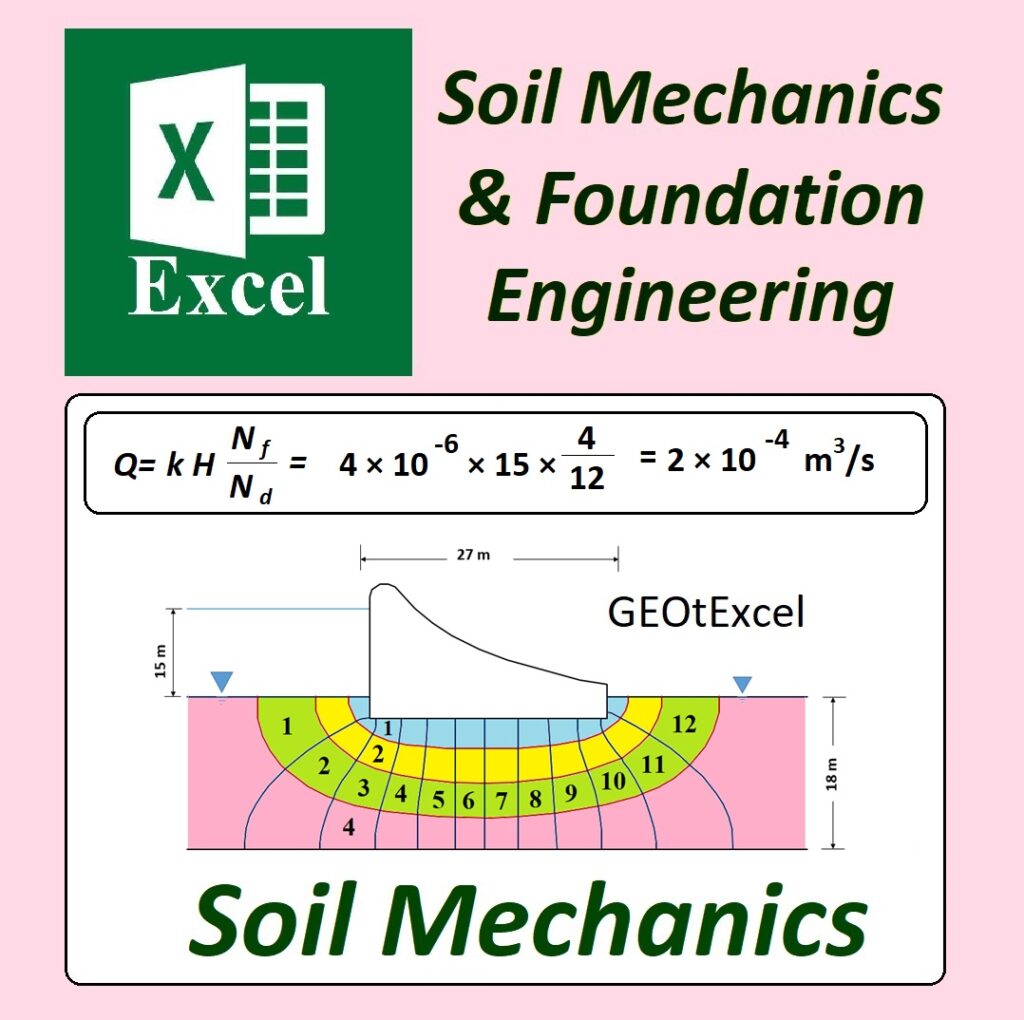
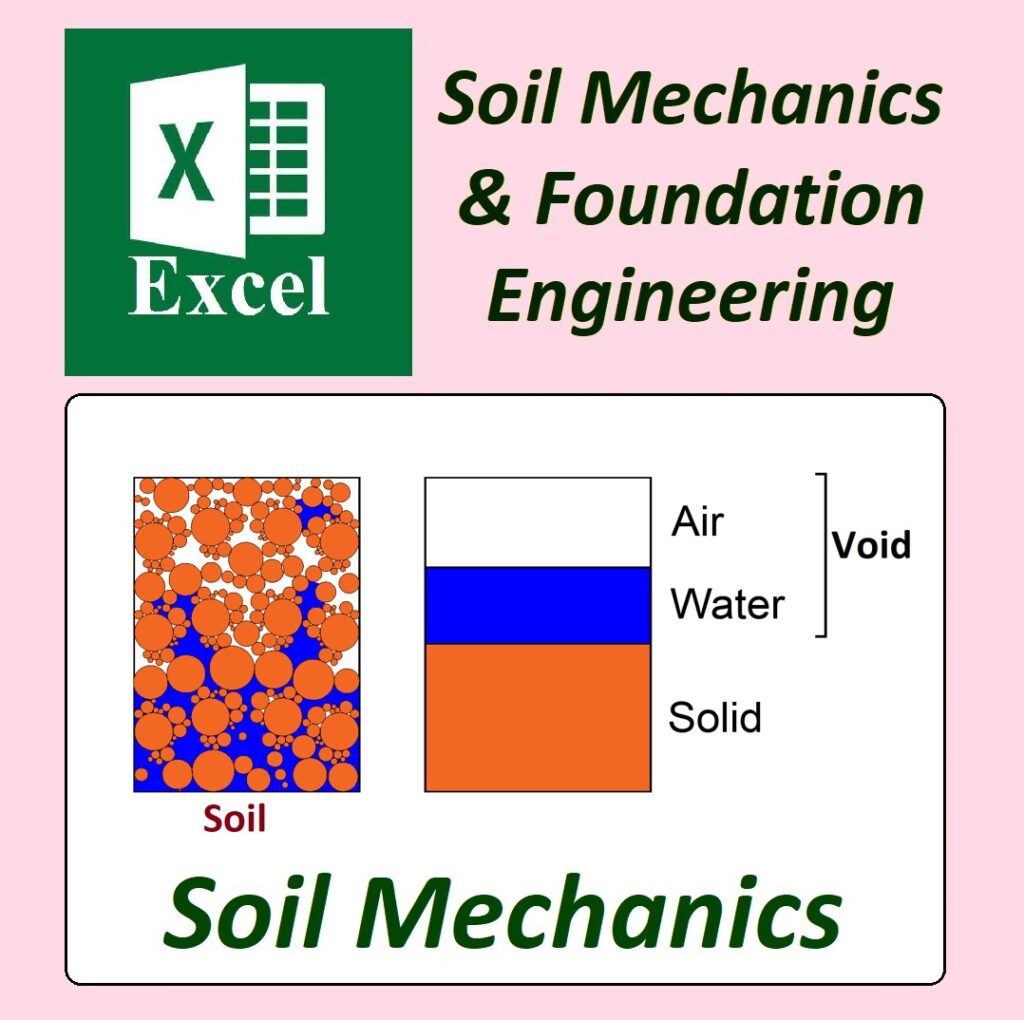
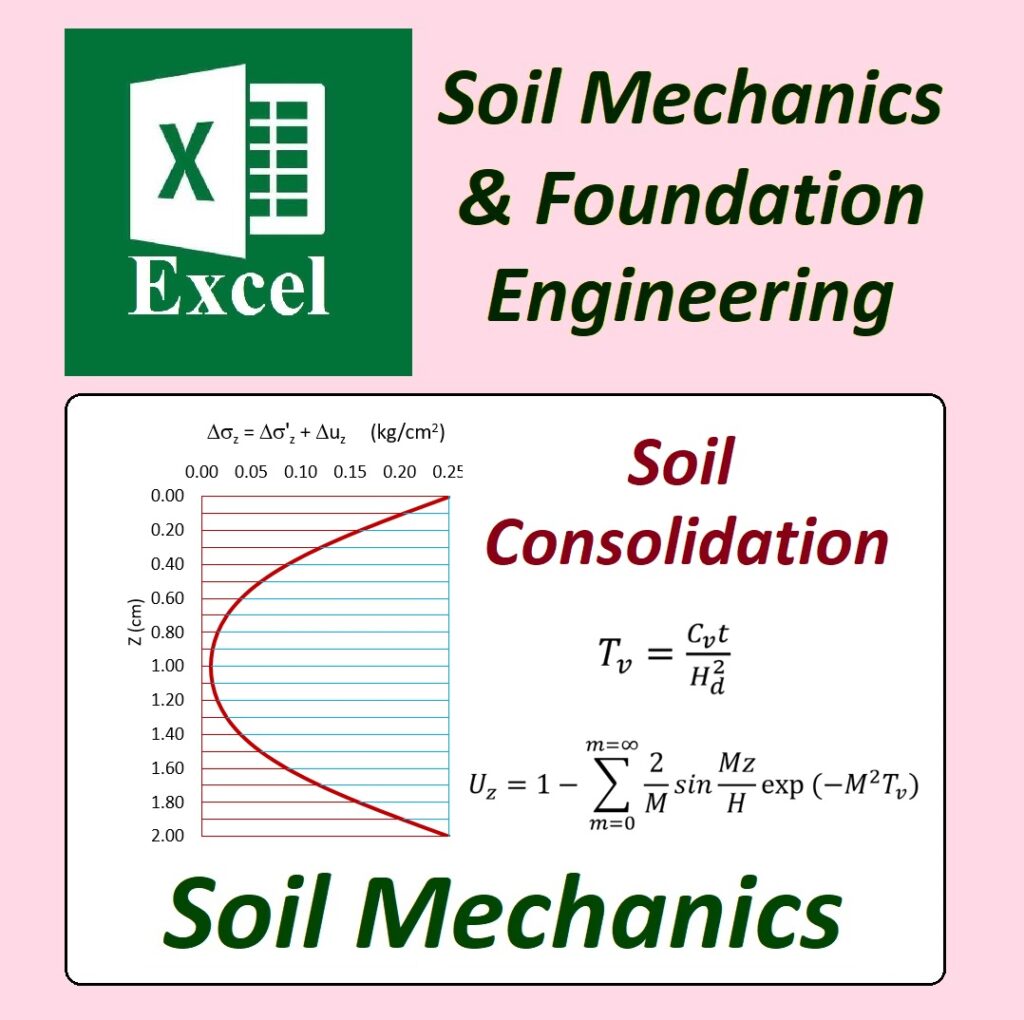
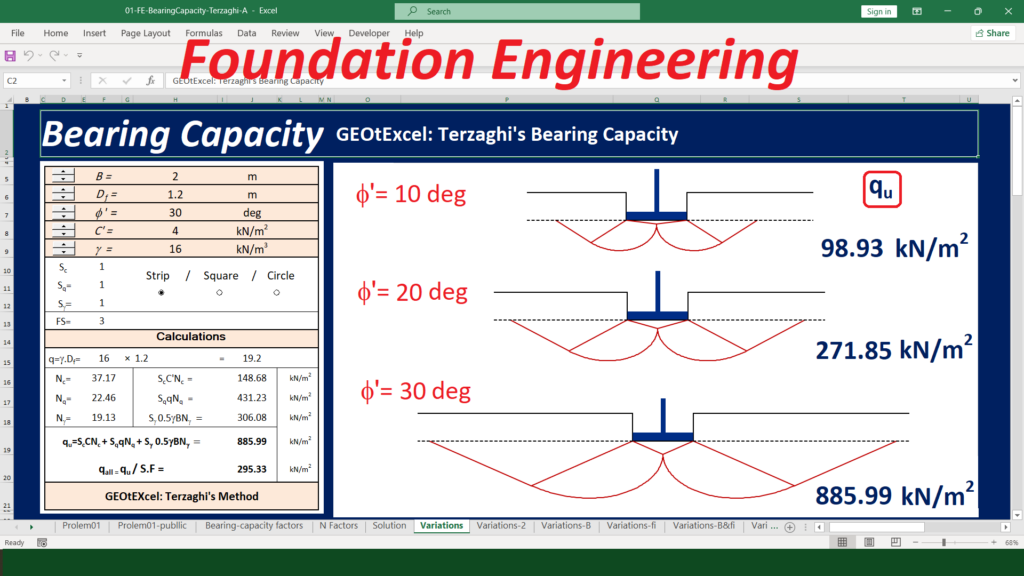
✅ Geotechnical Excel Spreadsheets – GEOtExcel (2025-1)
GEOtExcel 2025-1 is now easier to access, fully secure, and permanently usable on your personal computer. With this version, GEOtExcel brings an Excel-based desktop application packed with essential tools for soil mechanics, foundation engineering, and geotechnical testing.
What’s New in GEOtExcel 2025-1?
Thanks to valuable user feedback, the delivery method of GEOtExcel has been improved. The 2025-1 version now offers:
1️⃣ Lifetime, Unlimited Access: Use it anytime on your personal computer.
2️⃣ No Restrictions: Save, print, and manage data locally without any limitations.
3️⃣ Offline Access: No need for an internet connection or cloud service to use GEOtExcel.
Important Note
The current GEOtExcel 2025-1 version is fully functional and permanently usable on the registered computer.
(If future versions are released and you choose to upgrade, you’ll receive special discounts for existing users.)
How to Order GEOtExcel 2025
To begin the process of getting GEOtExcel 2025, follow these steps:
- Download the package:
Download Zip File - Unzip and open the package:
It contains two Excel files:
- File 1: GET ID: This file helps you extract your computer’s unique ID. Simply open the file and click the “Copy Computer ID” button.
- File 2: Agreement: This file contains 3 sheets:
- Sheet 1: Price List: Select the GEOtExcel files you wish to purchase, and the total price will be calculated automatically.
- Sheet 2: Customer & PC Info: Fill in your contact details and paste the copied Computer ID.
- Sheet 3: Agreement: Review and confirm your order details.
- Complete the required fields, then save the Agreement file and email it to:
📧 academy.dr.fahmi@gmail.com
Support and Assistance
Our support team is ready to assist you with the entire process, including payment, installation, and file delivery.
Why Choose GEOtExcel?
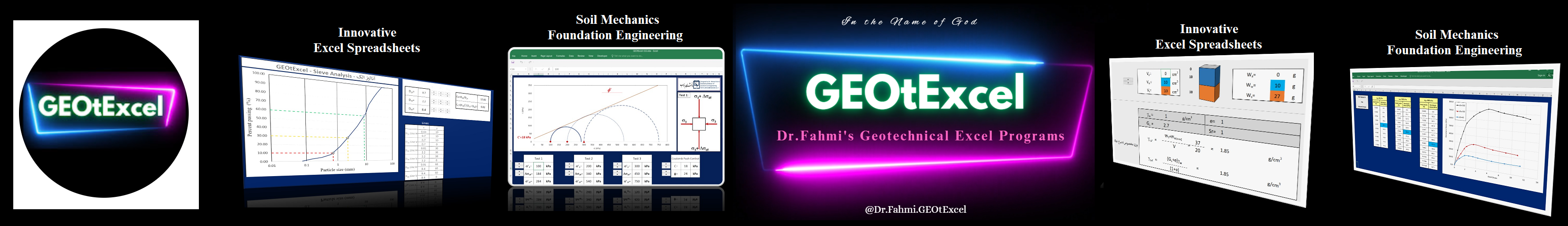
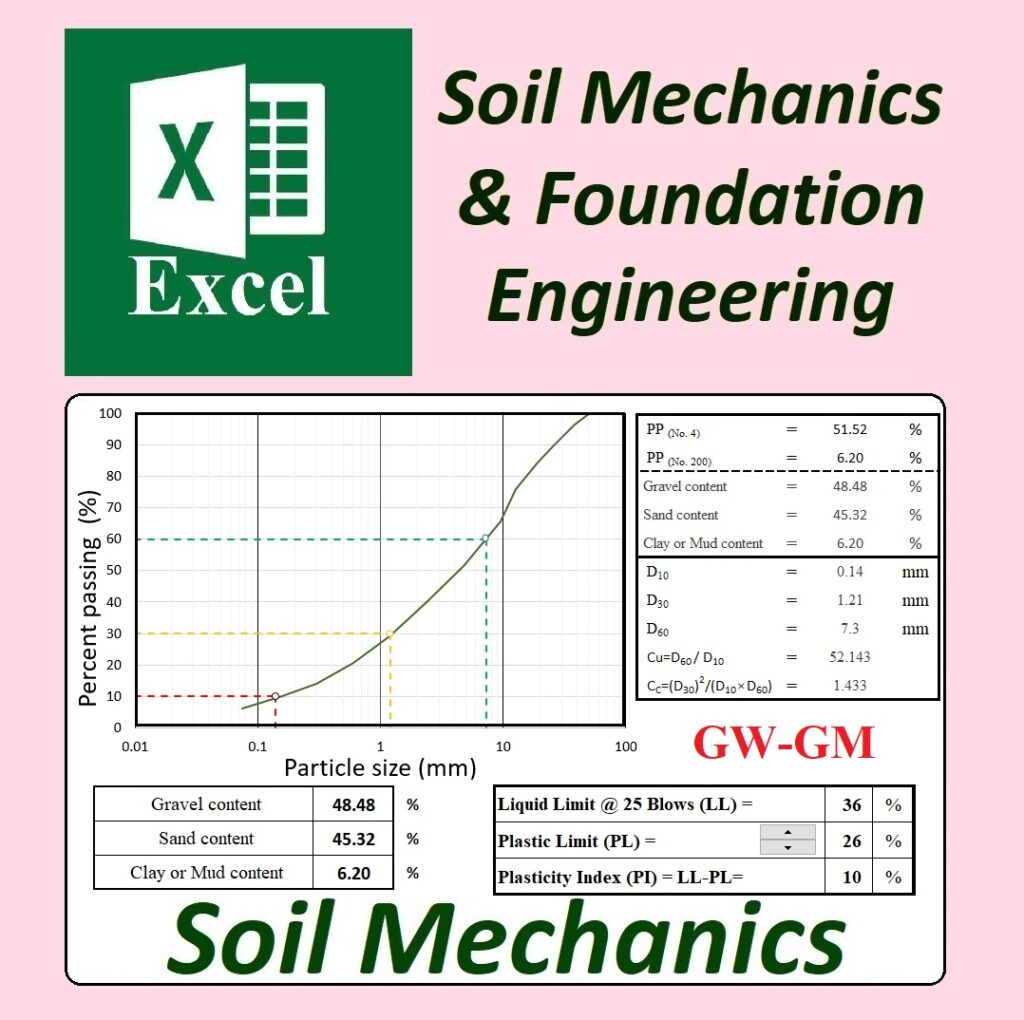
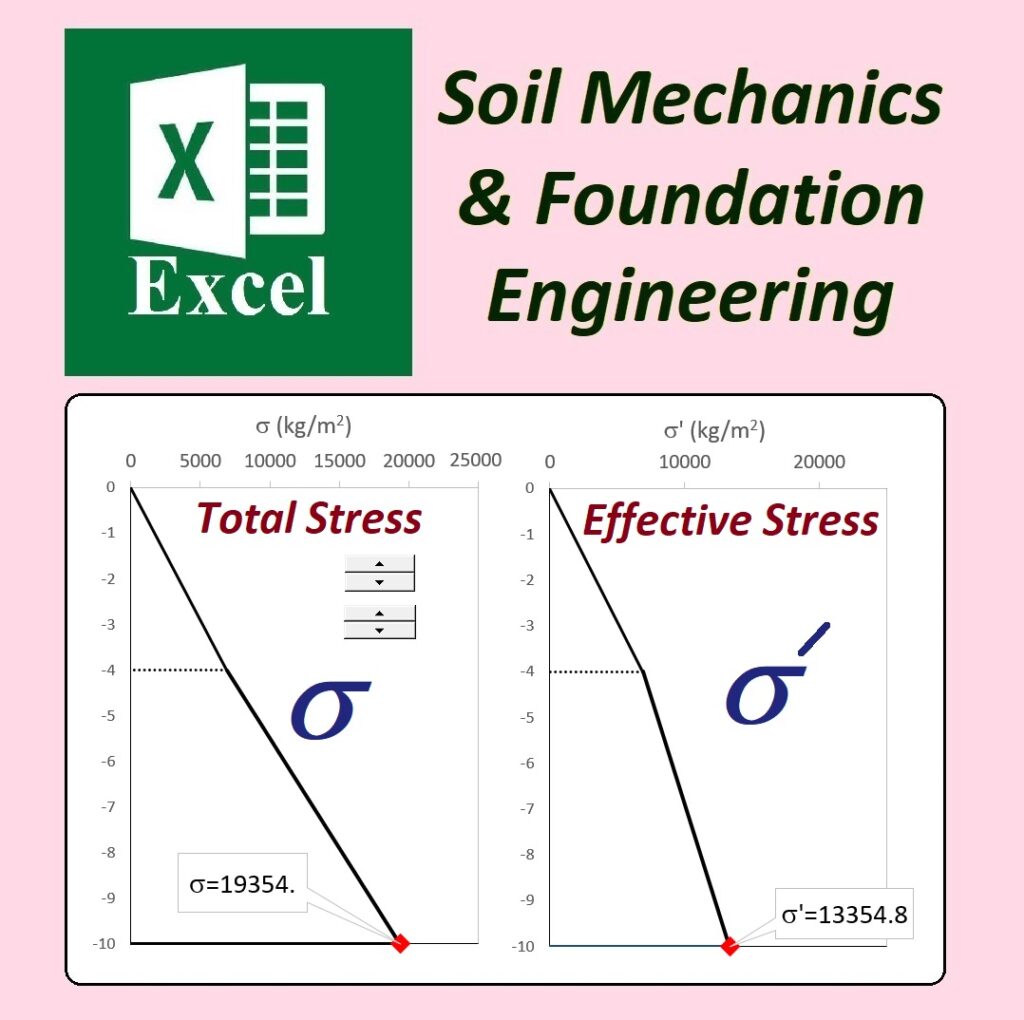
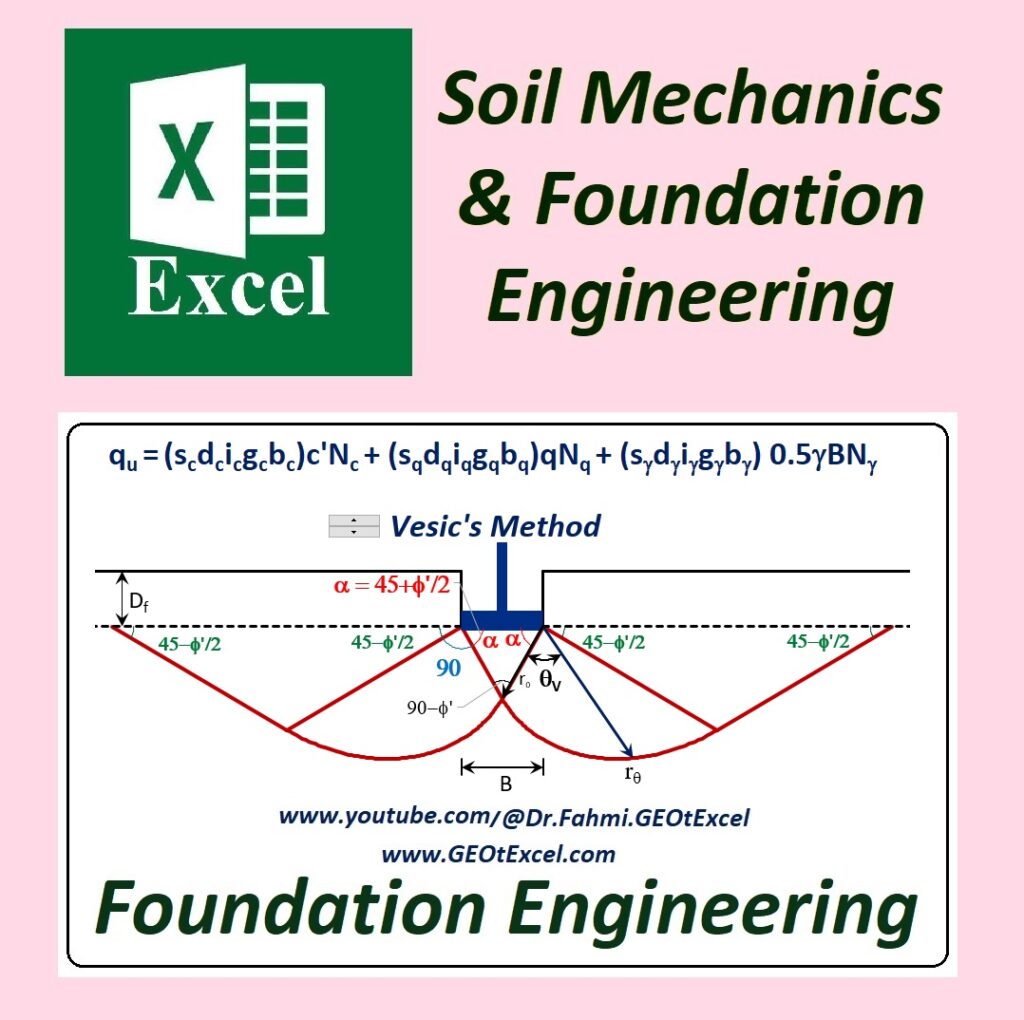
- Comprehensive: Includes 12 fields, 50 files, and over 470 Excel spreadsheets.
- Educational & Professional Quality: Created by Dr. Ahmad Fahmi, Assistant Professor at The University of Bonab, and CEO of GEOtExcel.
- Real-World Application: Designed for professionals and students working in geotechnical engineering, soil mechanics, and foundation engineering.
Follow GEOtExcel on Social Media:
Contact Dr. Ahmad Fahmi:
Assistant Professor, The University of Bonab
CEO of GEOtExcel (KAPA)
Email: academy.dr.fahmi@gmail.com
Stay Updated:
Subscribe to get the latest updates, lectures, and spreadsheets for soil mechanics, foundation engineering, and geotechnical testing.
➡️ Subscribe on YouTube