Video Link:
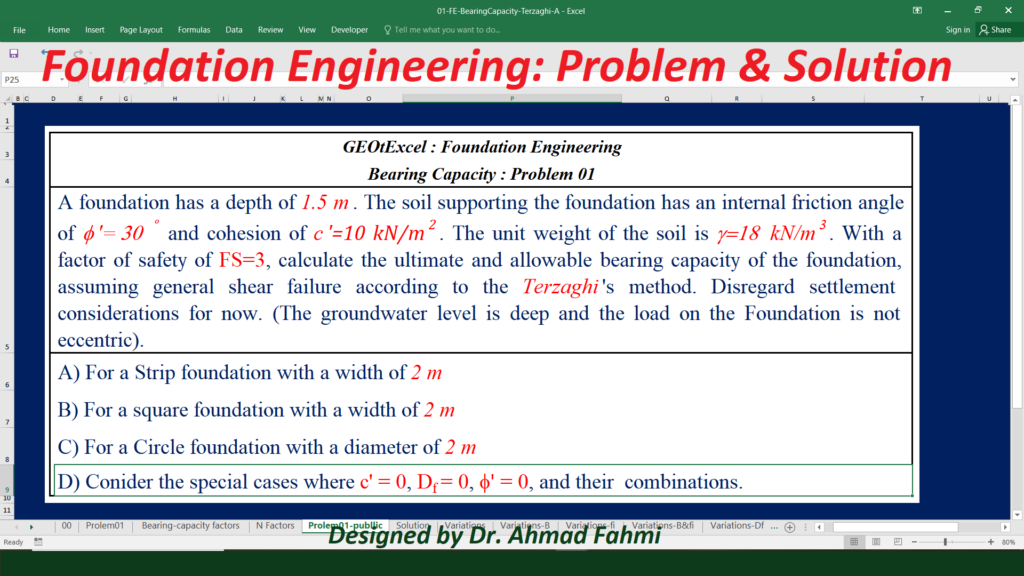
✅ Foundation Engineering Problem & Solution: “Bearing Capacity”
✅ Terzaghi’s Method: Strip, Square and Circle Foundations
✅ Unique Excel Spreadsheets: Geotechnical Excel Spreadsheets(GEOtExcel)
✅ Multi-Language Video: The subtitles in this video are accurate, so you can enable auto-translate to listen to the video in any language you prefer.
✅ Foundation Engineering: Bearing Capacity:
Foundation engineering is a vital discipline within civil engineering that focuses on the design and construction of foundations for various structures. A key element in this field is the bearing capacity of the soil, which refers to the soil’s ability to support the loads imposed by the structure. Assessing bearing capacity is essential to ensure the foundation remains stable and secure, thereby preventing excessive settlement or structural failure. This process involves determining the maximum load per unit area that the soil can withstand without experiencing shear failure. Factors influencing bearing capacity include soil type, moisture content, density, and the dimensions of the foundation. Thorough evaluation and enhancement of bearing capacity are crucial for the durability and stability of any construction project.
✅ In this educational and concept-focused video, you will see:
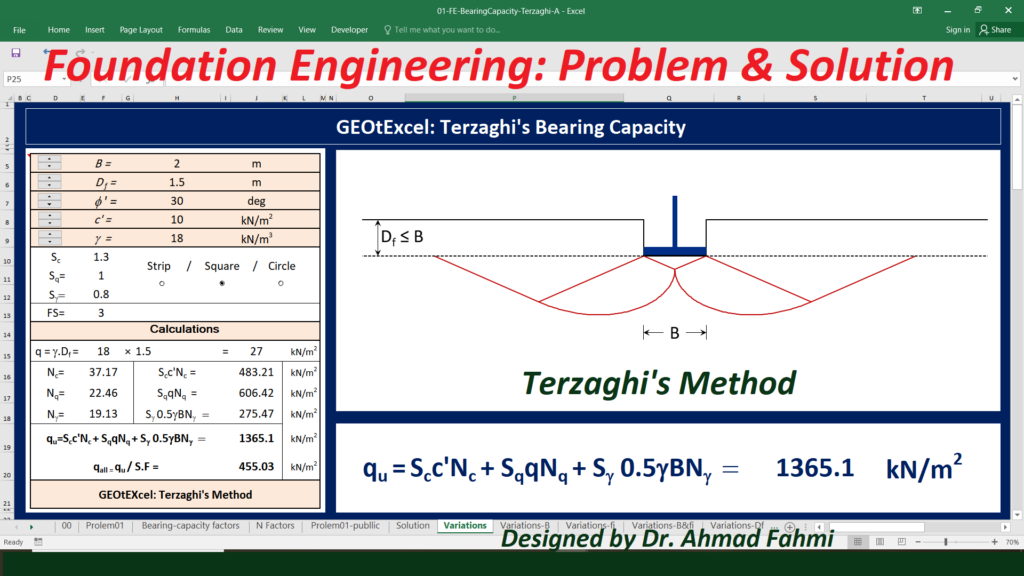
1) Calculating the Ultimate and Allowable Bearing Capacity of Strip, Square, and Circular Foundations Using Terzaghi’s Method
2) Considering the Variation of Ultimate Bearing Capacity Values with Different Soil-Foundation Parameters such as Foundation Depth, Foundation Width, Soil Cohesion, Soil Internal Friction Angle, and Soil Unit Weight
3) Considering Special Cases in the Calculation of Bearing Capacity, Such As:
- Non-Cohesive Soils (c’=0)
- Zero Foundation Depth (Df =0)
- Un-drained Soil Conditions (phi’=0)
- Combonation1: (c’=0 & Df = 0)
- Combonation2: (Df = 0 & phi’ = 0)
✅ Definitions:
For the Strip Foundations : B = The width of the foundation
For the Square Foundations : B = The dimension of each side of the foundation
For the Circle Foundations : B = The diameter of the foundation
Foundation Depth: Df = The depth of foundation measured from the ground surface
gamma = Unit Weight of Soil
c’ = Soil Cohesion or cu = Undrained Cohesion (phi =0)
phi’ = Angle of friction of soil
Sc , Sq & Sg : Shape Factors
FS = Factor of Safety
q = Surcharge: The soil above the bottom of the foundation can also be considered as being replaced by an equivalent surcharge (q= gamma . Df)
Nc = The bearing capacity factor related to the contribution of soil cohesion
Nq = The bearing capacity factor related to the contribution of surcharge
N(gamma) = The bearing capacity factor related to the contribution of unit weight
qu = Ultimate Bearing Capacity
q(all) = Allowable Bearing Capacity
Designed & Presented by Dr. Ahmad Fahmi
https://www.youtube.com/@Dr.Fahmi.GEOtExcel